Nanocapillaries for open tubular chromatographic separations of proteins in femtoliter to picoliter samples
- PMID: 19663450
- PMCID: PMC2802834
- DOI: 10.1021/ac901265t
Nanocapillaries for open tubular chromatographic separations of proteins in femtoliter to picoliter samples
Abstract
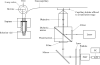
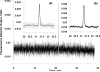
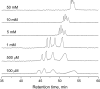
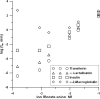
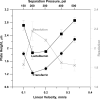
We have recently examined the potential of bare nanocapillaries for free solution DNA separations and demonstrated efficiencies exceeding 10(6) theoretical plates/m. In the present work, we demonstrate the use of bare and hydroxypropylcellulose (HPC) coated open tubular nanocapillaries for protein separations. Using 1.5 microm inner diameter (i.d.) capillary columns, hydrodynamically injecting femto- to picoliter volumes of fluorescent or fluorescent dye labeled protein samples, utilizing a pneumatically pressurized chamber containing 1.0 mM sodium tetraborate solution eluent (typically 200 psi) as the pump, and performing on-column detection using a simple laser-induced fluorescence detector, we demonstrate efficiencies of close to a million theoretical plates/m while generating single digit microliter volumes of waste for a complete chromatographic run. We achieve baseline resolution for a protein mixture consisting of transferrin, alpha-lactalbumin, insulin, and alpha-2-macroglobulin.
Figures




References
-
- Horvath CG, Preiss BA, Lipsky SR. Anal. Chem. 1967;39:1422–1428. - PubMed
-
- Horvath CG, Lipsky SR. Anal. Chem. 1969;41:1227–1234. - PubMed
-
- Ishii D. Jasco Report. 1974;11:1–7.
-
- Hibi K, Ishii D, Fujishima I, Takeuchi T, Nakanishi T. J. High Resolut. Chromatogr. Chromatogr. Commun. 1978;1:21–27.
-
- Tsuda T, Novtny MV. Anal. Chem. 1978;50:623–634.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

