The negative inotropic action of canrenone is mediated by L-type calcium current blockade and reduced intracellular calcium transients
- PMID: 19663883
- PMCID: PMC2757698
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00329.x
The negative inotropic action of canrenone is mediated by L-type calcium current blockade and reduced intracellular calcium transients
Abstract
Background and purpose: Adding spironolactone to standard therapy in heart failure reduces morbidity and mortality, but the underlying mechanisms are not fully understood. We analysed the effect of canrenone, the major active metabolite of spironolactone, on myocardial contractility and intracellular calcium homeostasis.
Experimental approach: Left ventricular papillary muscles and cardiomyocytes were isolated from male Wistar rats. Contractility of papillary muscles was assessed with force transducers, Ca(2+) transients by fluorescence and Ca(2+) fluxes by electrophysiological techniques.
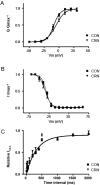
Key results: Canrenone (300-600 micromol L(-1)) reduced developed tension, maximum rate of tension increase and maximum rate of tension decay of papillary muscles. In cardiomyocytes, canrenone (50 micromol L(-1)) reduced cell shortening and L-type Ca(2+) channel current, whereas steady-state activation and inactivation, and reactivation curves were unchanged. Canrenone also decreased the Ca(2+) content of the sarcoplasmic reticulum, intracellular Ca(2+) transient amplitude and intracellular diastolic Ca(2+) concentration. However, the time course of [Ca(2+)](i) decline during transients evoked by caffeine was not affected by canrenone.
Conclusion and implications: Canrenone reduced L-type Ca(2+) channel current, amplitude of intracellular Ca(2+) transients and Ca(2+) content of sarcoplasmic reticulum in cardiomyocytes. These changes are likely to underlie the negative inotropic effect of canrenone.
Figures

References
-
- Barbato JC, Mulrow PJ, Shapiro JI, Franco-Saenz R. Rapid effects of aldosterone and spironolactone in the isolated working rat heart. Hypertension. 2002;40:130–135. - PubMed
-
- Baskin SI, Akera T, Puckett CR, Brody SL, Brody TM. Effect of potassium canrenoate on cardiac functions and (Na ++ K +)-activated ATPase. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973;143:495–498. - PubMed
-
- Bassani JWM, Yuan W, Bers DM. Fractional SR Ca release is regulated by trigger Ca and SR Ca content in cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1995b;268:C1313–C1319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

