A fractionation method to identify qauntitative changes in protein expression mediated by IGF-1 on the proteome of murine C2C12 myoblasts
- PMID: 19664293
- PMCID: PMC2732595
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-5956-7-28
A fractionation method to identify qauntitative changes in protein expression mediated by IGF-1 on the proteome of murine C2C12 myoblasts
Abstract
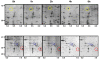
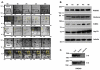
Although much is known about signal transduction downstream of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), relatively little is known about the global changes in protein expression induced by this hormone. In this study, the acute effects of IGF-1 on the proteome of murine C2C12 cells were examined. Cells were treated with IGF-1 for up to 24 hours, lysed, and fractionated into cytosolic, nuclear, and insoluble portions. Proteins from the cytosolic fraction were further separated using a new batch ion-exchange chromatography method to reduce sample complexity, followed by two-dimensional (2D) electrophoresis, and identification of selected proteins by mass spectrometry. PDQuest software was utilized to identify and catalogue temporal changes in protein expression during IGF-1 stimulation. In response to IGF-1 stimulation, expression of 23 proteins increased at least three-fold and expression of 17 proteins decreased at least three-fold compared with control un-stimulated C2C12 cells. Changes in expression of selected proteins from each group, including Rho-GDI, cofillin, RAD50, enolase, IkappaB kinase b (IkappaBKb) and Hsp70 were confirmed by Western blotting. Additionally, the position of 136 'landmark' proteins whose expression levels and physicochemical properties did not change appreciably or consistently during IGF-1 treatment were mapped and identified. This characterization of large-scale changes in protein expression in response to growth factor stimulation of C2C12 cells will further help to establish a comprehensive understanding of the networks and pathways involved in the action of IGF-1.
Figures
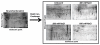


References
-
- Musaro A. Hyperglycemia-induced activation of human T-lymphocytes with de novo emergence of insulin receptors and generation of reactive oxygen species. Arch Ital Biol. 2005;143:243–248. - PubMed
-
- Glass DJ. Skeletal muscle hypertrophy and atrophy signaling pathways. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005;37:1974–1984. - PubMed
-
- Kurmasheva RT, Houghton PJ. IGF-I mediated survival pathways in normal and malignant cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1766:1–22. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

