Campesin, a thermostable antifungal peptide with highly potent antipathogenic activities
- PMID: 19664563
- PMCID: PMC7106469
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2009.03.013
Campesin, a thermostable antifungal peptide with highly potent antipathogenic activities
Abstract
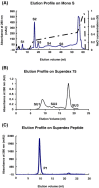
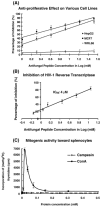
An 9.4-kDa antifungal peptide designated as campesin was isolated from seeds of the cabbage Brassica campestris. The isolation procedure involved affinity chromatography on Affi-gel blue gel, ion exchange chromatography on Q-Sepharose and Mono S, and gel filtration on Superdex 75 and Superdex Peptide. The peptide was adsorbed on the first three chromatographic media. It exerted an inhibitory action on mycelial growth including Fusarium oxysporum and Mycosphaerella arachidicola, with an IC(50) of 5.1 microM and 4.4 microM, respectively. The peptide was characterized by remarkable thermostability and pH stability. It inhibited proliferation of HepG2 and MCF cancer cells with an IC(50) of 6.4 microM and 1.8 microM, and the activity of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase with an IC(50) of 3.2 microM. It demonstrated lysolecithin binding activity.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A novel and exploitable antifungal peptide from kale (Brassica alboglabra) seeds.Peptides. 2008 Oct;29(10):1664-71. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2008.05.020. Epub 2008 Jul 1. Peptides. 2008. PMID: 18597893 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and characterization of an antifungal peptide with antiproliferative activity from seeds of Phaseolus vulgaris cv. 'Spotted Bean'.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007 Feb;74(1):125-30. doi: 10.1007/s00253-006-0650-9. Epub 2006 Dec 20. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 17177050
-
First isolation of an antifungal lipid transfer peptide from seeds of a Brassica species.Peptides. 2007 Aug;28(8):1514-9. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2007.06.028. Epub 2007 Jul 10. Peptides. 2007. PMID: 17692430
-
A peptide with potent antifungal and antiproliferative activities from Nepalese large red beans.Peptides. 2009 Dec;30(12):2089-94. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2009.08.017. Epub 2009 Aug 29. Peptides. 2009. PMID: 19720103
-
An antifungal peptide from baby lima bean.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2006 Dec;73(3):576-81. doi: 10.1007/s00253-006-0504-5. Epub 2006 Jul 19. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2006. PMID: 16850300
Cited by
-
Purification of an Antifungal Peptide from Seeds of Brassica oleracea var. gongylodes and Investigation of Its Antifungal Activity and Mechanism of Action.Molecules. 2019 Apr 4;24(7):1337. doi: 10.3390/molecules24071337. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30987412 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Broekaert W.F., Van Parijs J., Leyns F., Joos H., Peumans W.J. A chitin-binding lectin from stinging nettle rhizomes with antifungal properties. Science. 1989;245:1100–1102. - PubMed
-
- Cammue B.P.A., Thevissen K., Hendriks M., Eggermont K., Goderis I.J., Proost P., Van Damme J., Osborn R.W., Guerbette F., Kader J.C., Broekaert W.F. A potent antimicrobial protein from onion seeds showing sequence homology to plant lipid transfer protein. Plant. Physiol. 1995;109:445–455. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Leah R., Tommerup H., Svendsen I., Mundy J. Biochemical and molecular characterization of three barley seed proteins with antifungal properties. J. Biol. Chem. 1991;246:1564–1573. - PubMed
-
- Wang B., Shi X., Guo C., Ye X., Wang Z., Rao P. Isolation and purification of ribosome-inactivating proteins from bitter melon seeds by ion exchange chromatographic columns in series. Se Pu. 2004;22:543–546. - PubMed
-
- Gozia O., Ciopraga J., Bentia T., Lungu M., Zamfirescu I., Tudor R., Roseanu A., Nitu F. Antifungal properties of lectin and new chitinases from potato tuber. FEBS Lett. 1995;370:245–249. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

