An FcRn-dependent role for anti-flagellin immunoglobulin G in pathogenesis of colitis in mice
- PMID: 19664634
- PMCID: PMC2787451
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.07.059
An FcRn-dependent role for anti-flagellin immunoglobulin G in pathogenesis of colitis in mice
Abstract
Background & aims: The neonatal Fc receptor for immunoglobulin (Ig)G (FcRn) protects monomeric IgG from catabolism in parenchymal and hematopoietic cells during adult life. In dendritic cells, FcRn also promotes presentation of antigens in association with IgG. Because IgGs with anti-bacterial specificity are a hallmark of inflammatory bowel disease, we sought to determine their significance and relationship to FcRn expression in antigen-presenting cells, focusing on IgGs specific for flagellin.
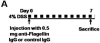
Methods: Levels of circulating anti-flagellin IgG were induced in wild-type and FcRn(-/-) mice, followed by induction of colitis with dextran sodium sulfate (DSS). Bone marrow chimera models were used to localize the site of FcRn action.
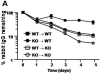
Results: Wild-type mice that received anti-flagellin IgG exhibited more severe colitis following administration of DSS, compared with mice that received control IgG. Wild-type mice immunized with flagellin exhibited significantly more severe colitis in response to DSS administration than that observed in similarly treated FcRn(-/-) mice. In chimera studies, FcRn(-/-) mice given wild-type bone marrow and immunized with flagellin exhibited significantly more colitis than wild-type mice given FcRn(-/-) bone marrow and immunized with flagellin. Serum anti-flagellin IgG levels were similar in both sets of chimeric mice, consistent with the equal participation of hematopoietic and nonhematopoeitic cells in FcRn-mediated IgG protection.
Conclusions: Anti-bacterial IgG antibodies are involved in the pathogenesis of colitis; this pathway requires FcRn in antigen presenting cells, the major subset of hematopoietic cells that express FcRn.
Figures




















Comment in
-
Pathogen-specific antibody: cause or effect?Gastroenterology. 2009 Nov;137(5):1570-3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.09.028. Epub 2009 Sep 27. Gastroenterology. 2009. PMID: 19789083 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
FcRn: from molecular interactions to regulation of IgG pharmacokinetics and functions.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2014;382:249-72. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-07911-0_12. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25116104 Review.
-
Neonatal Fc receptor for IgG (FcRn) regulates cross-presentation of IgG immune complexes by CD8-CD11b+ dendritic cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jun 14;108(24):9927-32. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1019037108. Epub 2011 May 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21628593 Free PMC article.
-
Conditional deletion of the MHC class I-related receptor FcRn reveals the sites of IgG homeostasis in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Feb 24;106(8):2788-93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0810796106. Epub 2009 Feb 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19188594 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal Fc receptor promotes immune complex-mediated glomerular disease.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014 May;25(5):918-25. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013050498. Epub 2013 Dec 19. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24357670 Free PMC article.
-
New functions of the MHC class I-related Fc receptor, FcRn.Biochem Soc Trans. 1997 May;25(2):481-6. doi: 10.1042/bst0250481. Biochem Soc Trans. 1997. PMID: 9191140 Review.
Cited by
-
Neonatal Fc Receptor Regulation of Lung Immunoglobulin and CD103+ Dendritic Cells Confers Transient Susceptibility to Tuberculosis.Infect Immun. 2016 Sep 19;84(10):2914-21. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00533-16. Print 2016 Oct. Infect Immun. 2016. PMID: 27481246 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal Fc receptor expression in macrophages is indispensable for IgG homeostasis.MAbs. 2019 Jul;11(5):848-860. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2019.1602459. Epub 2019 Apr 30. MAbs. 2019. PMID: 30964743 Free PMC article.
-
Human Microbiota Flagellins Drive Adaptive Immune Responses in Crohn's Disease.Gastroenterology. 2021 Aug;161(2):522-535.e6. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.03.064. Epub 2021 May 7. Gastroenterology. 2021. PMID: 33844987 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccination with recombinant Lactococcus lactis expressing HA1-IgY Fc fusion protein provides protective mucosal immunity against H9N2 avian influenza virus in chickens.Virol J. 2023 Apr 21;20(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12985-023-02044-9. Virol J. 2023. PMID: 37085816 Free PMC article.
-
Infectious etiopathogenesis of Crohn's disease.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Sep 14;20(34):12102-17. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i34.12102. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25232246 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Strober W, Fuss IJ, Blumberg RS. The immunology of mucosal models of inflammation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:495–549. - PubMed
-
- Cho JH. The genetics and immunopathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:458–466. - PubMed
-
- Onderdonk AB, Hermos JA, Bartlett JG. The role of the intestinal microflora in experimental colitis. Am J Clin Nutr. 1977;30:1819–1825. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

