Alpha-lipoic acid as a dietary supplement: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential
- PMID: 19664690
- PMCID: PMC2756298
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2009.07.026
Alpha-lipoic acid as a dietary supplement: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential
Abstract
Alpha-lipoic acid (LA) has become a common ingredient in multivitamin formulas, anti-aging supplements, and even pet food. It is well-defined as a therapy for preventing diabetic polyneuropathies, and scavenges free radicals, chelates metals, and restores intracellular glutathione levels which otherwise decline with age. How do the biochemical properties of LA relate to its biological effects? Herein, we review the molecular mechanisms of LA discovered using cell and animal models, and the effects of LA on human subjects. Though LA has long been touted as an antioxidant, it has also been shown to improve glucose and ascorbate handling, increase eNOS activity, activate Phase II detoxification via the transcription factor Nrf2, and lower expression of MMP-9 and VCAM-1 through repression of NF-kappa B. LA and its reduced form, dihydrolipoic acid, may use their chemical properties as a redox couple to alter protein conformations by forming mixed disulfides. Beneficial effects are achieved with low micromolar levels of LA, suggesting that some of its therapeutic potential extends beyond the strict definition of an antioxidant. Current trials are investigating whether these beneficial properties of LA make it an appropriate treatment not just for diabetes, but also for the prevention of vascular disease, hypertension, and inflammation.
Figures



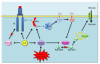
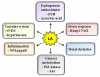
Similar articles
-
Molecular aspects of lipoic acid in the prevention of diabetes complications.Nutrition. 2001 Oct;17(10):888-95. doi: 10.1016/s0899-9007(01)00658-x. Nutrition. 2001. PMID: 11684397 Review.
-
Antioxidant properties of an endogenous thiol: Alpha-lipoic acid, useful in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2009 Nov;54(5):391-8. doi: 10.1097/fjc.0b013e3181be7554. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19998523 Review.
-
Alpha-lipoic acid supplementation and diabetes.Nutr Rev. 2008 Nov;66(11):646-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.2008.00118.x. Nutr Rev. 2008. Retraction in: Nutr Rev. 2012 Aug;70(8):482. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.2012.00507.x. PMID: 19019027 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
-
Lipoic acid - biological activity and therapeutic potential.Pharmacol Rep. 2011;63(4):849-58. doi: 10.1016/s1734-1140(11)70600-4. Pharmacol Rep. 2011. PMID: 22001972 Review.
-
[Lipoic acid: physiological role and prospects for clinical application].Vopr Pitan. 2019;88(4):6-11. doi: 10.24411/0042-8833-2019-10035. Epub 2019 Jul 15. Vopr Pitan. 2019. PMID: 31722135 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
The protective effect of lipoic acid on selected cardiovascular diseases caused by age-related oxidative stress.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:313021. doi: 10.1155/2015/313021. Epub 2015 Apr 8. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015. PMID: 25949771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary Antioxidants in the Treatment of Male Infertility: Counteracting Oxidative Stress.Biology (Basel). 2021 Mar 20;10(3):241. doi: 10.3390/biology10030241. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33804600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tetrahedral (T) Closed-Shell Cluster of 29 Silver Atoms & 12 Lipoate Ligands, [Ag29(R-α-LA)12](3-): Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity.ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2018 Apr 27;1(4):1595-1602. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.8b00069. Epub 2018 Mar 26. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2018. PMID: 32999995 Free PMC article.
-
α-Lipoic acid chemistry: the past 70 years.RSC Adv. 2023 Dec 13;13(51):36346-36363. doi: 10.1039/d3ra07140e. eCollection 2023 Dec 8. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 38093731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alpha-lipoic acid attenuates atherosclerotic lesions and inhibits proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells through targeting of the Ras/MEK/ERK signaling pathway.Mol Biol Rep. 2012 Jun;39(6):6857-66. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-1511-5. Mol Biol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22302393
References
-
- Smith AR, Shenvi SV, Widlansky M, Suh JH, Hagen TM. Lipoic acid as a potential therapy for chronic diseases associated with oxidative stress. Curr Med Chem. 2004;11:1135–46. - PubMed
-
- Scott BC, Aruoma OI, Evans PJ, O’Neill C, Van der Vliet A, Cross CE, Tritschler H, Halliwell B. Lipoic and dihydrolipoic acids as antioxidants. A critical evaluation. Free Radic Res. 1994;20:119–33. - PubMed
-
- Devasagayam TP, Subramanian M, Pradhan DS, Sies H. Prevention of singlet oxygen-induced DNA damage by lipoate. Chem Biol Interact. 1993;86:79–92. - PubMed
-
- Liu J, Head E, Gharib AM, Yuan W, Ingersoll RT, Hagen TM, Cotman CW, Ames BN. Memory loss in old rats is associated with brain mitochondrial decay and RNA/DNA oxidation: partial reversal by feeding acetyl-L-carnitine and/or R-alpha -lipoic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:2356–61. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

