Myosin VI dimerization triggers an unfolding of a three-helix bundle in order to extend its reach
- PMID: 19664948
- PMCID: PMC2756668
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.07.010
Myosin VI dimerization triggers an unfolding of a three-helix bundle in order to extend its reach
Abstract
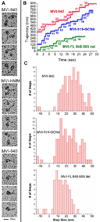
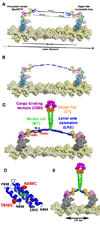
Myosin VI challenges the prevailing theory of how myosin motors move on actin: the lever arm hypothesis. While the reverse directionality and large powerstroke of myosin VI can be attributed to unusual properties of a subdomain of the motor (converter with a unique insert), these adaptations cannot account for the large step size on actin. Either the lever arm hypothesis needs modification, or myosin VI has some unique form of extension of its lever arm. We determined the structure of the region immediately distal to the lever arm of the motor and show that it is a three-helix bundle. Based on C-terminal truncations that display the normal range of step sizes on actin, CD, fluorescence studies, and a partial deletion of the bundle, we demonstrate that this bundle unfolds upon dimerization of two myosin VI monomers. This unconventional mechanism generates an extension of the lever arm of myosin VI.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Myosin VI must dimerize and deploy its unusual lever arm in order to perform its cellular roles.Cell Rep. 2014 Sep 11;8(5):1522-32. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.07.041. Epub 2014 Aug 21. Cell Rep. 2014. PMID: 25159143 Free PMC article.
-
The unique insert at the end of the myosin VI motor is the sole determinant of directionality.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jan 16;104(3):778-83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0610066104. Epub 2007 Jan 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17213313 Free PMC article.
-
The power stroke of myosin VI and the basis of reverse directionality.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jan 16;104(3):772-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0610144104. Epub 2006 Dec 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17182734 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin VI: an innovative motor that challenged the swinging lever arm hypothesis.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Feb;11(2):128-37. doi: 10.1038/nrm2833. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20094053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myosin VI rewrites the rules for myosin motors.Cell. 2010 May 14;141(4):573-82. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.04.028. Cell. 2010. PMID: 20478251 Review.
Cited by
-
Processive steps in the reverse direction require uncoupling of the lead head lever arm of myosin VI.Mol Cell. 2012 Oct 12;48(1):75-86. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.07.034. Epub 2012 Aug 30. Mol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22940248 Free PMC article.
-
Detailed tuning of structure and intramolecular communication are dispensable for processive motion of myosin VI.Biophys J. 2011 Jan 19;100(2):430-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.11.045. Biophys J. 2011. PMID: 21244839 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin V executes steps of variable length via structurally constrained diffusion.Elife. 2020 Jan 15;9:e51569. doi: 10.7554/eLife.51569. Elife. 2020. PMID: 31939739 Free PMC article.
-
Plus-end directed myosins accelerate actin filament sliding by single-headed myosin VI.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2012 Jan;69(1):59-69. doi: 10.1002/cm.21002. Epub 2012 Jan 9. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2012. PMID: 22213699 Free PMC article.
-
How myosin motors power cellular functions: an exciting journey from structure to function: based on a lecture delivered at the 34th FEBS Congress in Prague, Czech Republic, July 2009.FEBS J. 2012 Feb;279(4):551-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08449.x. Epub 2012 Jan 9. FEBS J. 2012. PMID: 22171985 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams PD, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Hung L-W, Ioerger TR, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Read RJ, Sacchettini JC, Sauter NK, Terwilliger TC. PHENIX: building new software for automated crystallographic structure determination. Acta Cryst. 2002;D58:1948–1954. - PubMed
-
- Akey DL, Malashkevich VN, Kim PS. Buried polar residues in coiled-coil interfaces. Biochemistry. 2001;40:6352–6360. - PubMed
-
- Altman D, Sweeney HL, Spudich JA. The mechanism of myosin VI translocation and its load-induced anchoring. Cell. 2004;116:737–749. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

