Phosphoproteomic analysis of human embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 19664994
- PMCID: PMC2726933
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2009.06.002
Phosphoproteomic analysis of human embryonic stem cells
Abstract
Protein phosphorylation, while critical to cellular behavior, has been undercharacterized in pluripotent cells. Therefore, we performed phosphoproteomic analyses of human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) and their differentiated derivatives. A total of 2546 phosphorylation sites were identified on 1602 phosphoproteins; 389 proteins contained more phosphorylation site identifications in undifferentiated hESCs, whereas 540 contained more such identifications in differentiated derivatives. Phosphoproteins in receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) signaling pathways were numerous in undifferentiated hESCs. Cellular assays corroborated this observation by showing that multiple RTKs cooperatively supported undifferentiated hESCs. In addition to bFGF, EGFR, VEGFR, and PDGFR activation was critical to the undifferentiated state of hESCs. PDGF-AA complemented a subthreshold bFGF concentration to maintain undifferentiated hESCs. Also consistent with phosphoproteomics, JNK activity participated in maintenance of undifferentiated hESCs. These results support the utility of phosphoproteomic data, provide guidance for investigating protein function in hESCs, and complement transcriptomics/epigenetics for broadening our understanding of hESC fate determination.
Figures
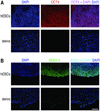
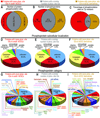
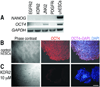
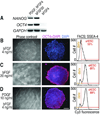
Comment in
-
Unraveling the human embryonic stem cell phosphoproteome.Cell Stem Cell. 2009 Aug 7;5(2):126-8. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2009.07.007. Cell Stem Cell. 2009. PMID: 19664982
References
-
- Adewumi O, Aflatoonian B, Ahrlund-Richter L, Amit M, Andrews PW, Beighton G, Bello PA, Benvenisty N, Berry LS, Bevan S, et al. Characterization of human embryonic stem cell lines by the International Stem Cell Initiative. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:803–816. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong L, Hughes O, Yung S, Hyslop L, Stewart R, Wappler I, Peters H, Walter T, Stojkovic P, Evans J, et al. The role of PI3K/AKT, MAPK/ERK and NFkappabeta signalling in the maintenance of human embryonic stem cell pluripotency and viability highlighted by transcriptional profiling and functional analysis. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15:1894–1913. - PubMed
-
- Beattie GM, Lopez AD, Bucay N, Hinton A, Firpo MT, King CC, Hayek A. Activin A maintains pluripotency of human embryonic stem cells in the absence of feeder layers. Stem Cells. 2005;23:489–495. - PubMed
-
- Belotserkovskaya R, Oh S, Bondarenko VA, Orphanides G, Studitsky VM, Reinberg D. FACT facilitates transcription-dependent nucleosome alteration. Science. 2003;301:1090–1093. - PubMed
-
- Bendall SC, Stewart MH, Menendez P, George D, Vijayaragavan K, Werbowetski-Ogilvie T, Ramos-Mejia V, Rouleau A, Yang J, Bosse M, et al. IGF and FGF cooperatively establish the regulatory stem cell niche of pluripotent human cells in vitro. Nature. 2007;448:1015–1021. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

