p38(MAPK): stress responses from molecular mechanisms to therapeutics
- PMID: 19665431
- PMCID: PMC3016890
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmed.2009.06.005
p38(MAPK): stress responses from molecular mechanisms to therapeutics
Abstract
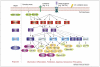
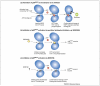
The p38(MAPK) protein kinases affect a variety of intracellular responses, with well-recognized roles in inflammation, cell-cycle regulation, cell death, development, differentiation, senescence and tumorigenesis. In this review, we examine the regulatory and effector components of this pathway, focusing on their emerging roles in biological processes involved in different pathologies. We summarize how this pathway has been exploited for the development of therapeutics and discuss the potential obstacles of targeting this promiscuous protein kinase pathway for the treatment of different diseases. Furthermore, we discuss how the p38(MAPK) pathway might be best exploited for the development of more effective therapeutics with minimal side effects in a range of specific disease settings.
Figures
References
-
- Kaminska B. MAPK signalling pathways as molecular targets for anti-inflammatory therapy–from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic benefits. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2005;1754:253–262. - PubMed
-
- Han J, et al. A MAP kinase targeted by endotoxin and hyperosmolarity in mammalian cells. Science. 1994;265:808–811. - PubMed
-
- Jiang Y, et al. Characterization of the structure and function of the fourth member of p38 group mitogen-activated protein kinases, p38δ. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:30122–30128. - PubMed
-
- Raman M, et al. Differential regulation and properties of MAPKs. Oncogene. 2007;26:3100–3112. - PubMed
-
- Ono K, Han J. The p38 signal transduction pathway: activation and function. Cell. Signal. 2000;12:1–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

