The phenomenon of task-irrelevant perceptual learning
- PMID: 19665471
- PMCID: PMC2764800
- DOI: 10.1016/j.visres.2009.08.003
The phenomenon of task-irrelevant perceptual learning
Abstract
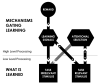
Task-irrelevant perceptual learning (TIPL) has captured a growing interest in the field of perceptual learning. The basic phenomenon is that stimulus features that are irrelevant to a subject's task (i.e. convey no useful information to that task) can be learned due to their consistent presentation during task-performance. Here we review recent research on TIPL and focus on two key aspects of TIPL; (1) the mechanisms gating learning in TIPL, and (2) what is learned through TIPL. We show that TIPL is gated by learning signals that are triggered from task processing or by rewards. These learning signals operate to enhance processing of individual stimulus features and appear to result in plasticity in early stages of visual processing. Furthermore, we discuss recent research that demonstrates that TIPL is not in opposition to theories of attention but instead that TIPL operates in concert with attention. Where attentional learning is best to enhance (or suppress) processing of stimuli of known task relevance, TIPL serves to enhance perception of stimuli that are originally inadequately processed by the brain.
Figures
References
-
- Ahissar M, Hochstein S. The reverse hierarchy theory of visual perceptual learning. Trends Cogn Sci. 2004;8(10):457–464. - PubMed
-
- Chun MM. Contextual cueing of visual attention. Trends Cogn Sci. 2000;4(5):170–178. - PubMed
-
- Chun MM, Marois R. The dark side of visual attention. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2002;12(2):184–189. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

