The ectopic expression of Pax4 in the mouse pancreas converts progenitor cells into alpha and subsequently beta cells
- PMID: 19665969
- PMCID: PMC2792203
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.05.035
The ectopic expression of Pax4 in the mouse pancreas converts progenitor cells into alpha and subsequently beta cells
Abstract
We have previously reported that the loss of Arx and/or Pax4 gene activity leads to a shift in the fate of the different endocrine cell subtypes in the mouse pancreas, without affecting the total endocrine cell numbers. Here, we conditionally and ectopically express Pax4 using different cell-specific promoters and demonstrate that Pax4 forces endocrine precursor cells, as well as mature alpha cells, to adopt a beta cell destiny. This results in a glucagon deficiency that provokes a compensatory and continuous glucagon+ cell neogenesis requiring the re-expression of the proendocrine gene Ngn3. However, the newly formed alpha cells fail to correct the hypoglucagonemia since they subsequently acquire a beta cell phenotype upon Pax4 ectopic expression. Notably, this cycle of neogenesis and redifferentiation caused by ectopic expression of Pax4 in alpha cells is capable of restoring a functional beta cell mass and curing diabetes in animals that have been chemically depleted of beta cells.
Figures
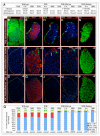
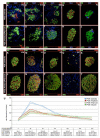
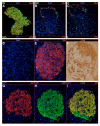
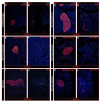

Comment in
-
Alpha cells beget beta cells.Cell. 2009 Aug 7;138(3):424-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.07.022. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19665963
-
GABA signaling: A route to new pancreatic β cells.Cell Res. 2017 Mar;27(3):309-310. doi: 10.1038/cr.2017.20. Epub 2017 Feb 10. Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 28186081 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahlgren U, Jonsson J, Edlund H. The morphogenesis of the pancreatic mesenchyme is uncoupled from that of the pancreatic epithelium in IPF1/PDX1-deficient mice. Development. 1996;122:1409–1416. - PubMed
-
- Ashery-Padan R, Zhou X, Marquardt T, Herrera P, Toube L, Berry A, Gruss P. Conditional inactivation of Pax6 in the pancreas causes early onset of diabetes. Dev Biol. 2004;269:479–488. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

