Psychotropic medication use and risk of adverse cardiovascular events in women with suspected coronary artery disease: outcomes from the Women's Ischemia Syndrome Evaluation (WISE) study
- PMID: 19666461
- PMCID: PMC2784030
- DOI: 10.1136/hrt.2009.176040
Psychotropic medication use and risk of adverse cardiovascular events in women with suspected coronary artery disease: outcomes from the Women's Ischemia Syndrome Evaluation (WISE) study
Abstract
Objective: This study investigated the relation between psychotropic medication use and adverse cardiovascular (CV) events in women with symptoms of myocardial ischaemia undergoing coronary angiography.
Method: Women enrolled in the Women's Ischemia Syndrome Evaluation (WISE) were classified into one of four groups according to their reported antidepressant and anxiolytic medication usage at study intake: (1) no medication (n = 352); (2) anxiolytics only (n = 67); (3) antidepressants only (n = 58); and (4) combined antidepressant and anxiolytics (n = 39). Participants were followed prospectively for the development of adverse CV events (for example, hospitalisations for non-fatal myocardial infarction, stroke, congestive heart failure and unstable angina) or all-cause mortality over a median of 5.9 years.
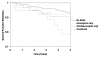
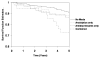
Results: Use of antidepressant medication was associated with subsequent CV events (HR 2.16, 95% CI 1.21 to 3.93) and death (HR 2.15, 95% CI 1.16 to 3.98) but baseline anxiolytic use alone did not predict subsequent CV events and death. In a final regression model that included demographics, depression and anxiety symptoms, and risk factors for cardiovascular disease, women in the combined medication group (that is, antidepressants and anxiolytics) had higher risk for CV events (HR 3.98, CI 1.74 to 9.10, p = 0.001 and all-cause mortality (HR 4.70, CI 1.7 to 2.97, p = 0.003) compared to those using neither medication. Kaplan-Meier survival curves indicated that there was a significant difference in mortality among the four medication groups (p = 0.001).
Conclusions: These data suggest that factors related to psychotropic medication such as depression refractory to treatment, or medication use itself, are associated with adverse CV events in women with suspected myocardial ischaemia.
Figures
Comment in
-
Psychotropic medication: curing illness or creating problems?Heart. 2009 Dec;95(23):1893-4. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2009.179127. Epub 2009 Sep 23. Heart. 2009. PMID: 19778922 No abstract available.
References
-
- Blumenthal JA, Lett HS, Babyak MA, White W, Smith PK, Mark DB, et al. Depression as a risk factor for mortality after coronary artery bypass surgery. Lancet. 2003;362(9384):604–9. - PubMed
-
- Frasure-Smith N, Lesperance F. Depression and anxiety as predictors of 2-year cardiac events in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2008;65(1):62–71. - PubMed
-
- Lesperance F, Frasure-Smith N, Koszycki D, Laliberte MA, van Zyl LT, Baker B, et al. Effects of citalopram and interpersonal psychotherapy on depression in patients with coronary artery disease: the Canadian Cardiac Randomized Evaluation of Antidepressant and Psychotherapy Efficacy (CREATE) trial. JAMA. 2007;297(4):367–79. - PubMed
-
- Glassman AH, O’Connor CM, Califf RM, Swedberg K, Schwartz P, Bigger JT, Jr., et al. Sertraline treatment of major depression in patients with acute MI or unstable angina. JAMA. 2002;288(6):701–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01 HV068161/HV/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL064829/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HV068163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL649241/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HV068162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL069751/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32HL69751/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U0164829,/PHS HHS/United States
- U01 HL064914/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL064924/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL649141/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HV-68162/HV/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HV068164/HV/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HV068163/HV/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HV-68163/HV/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HV068162/HV/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical