NEMO-binding domains of both IKKalpha and IKKbeta regulate IkappaB kinase complex assembly and classical NF-kappaB activation
- PMID: 19666475
- PMCID: PMC2785688
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.047563
NEMO-binding domains of both IKKalpha and IKKbeta regulate IkappaB kinase complex assembly and classical NF-kappaB activation
Abstract
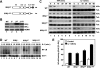
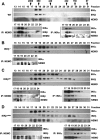
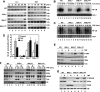
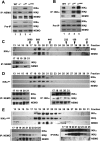
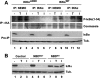
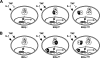
Proinflammatory NF-kappaB activation requires the IkappaB (inhibitor of NF-kappaB) kinase (IKK) complex that contains two catalytic subunits named IKKalpha and IKKbeta and a regulatory subunit named NF-kappaB essential modulator (NEMO). NEMO and IKKbeta are essential for tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-induced NF-kappaB activation, and we recently demonstrated that NEMO and IKKalpha are sufficient for interleukin (IL)-1-induced signaling. IKKalpha and IKKbeta both contain a functional NEMO-binding domain (NBD); however, the role of NEMO association with each kinase in NF-kappaB signaling and IKK complex formation remains unclear. To address this question, we stably reconstituted IKKalpha(-/-) and IKKbeta(-/-) murine embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) with wild-type (WT) or NBD-deficient (DeltaNBD) versions of IKKalpha and IKKbeta, respectively. TNF-induced classical NF-kappaB activation in IKKbeta(-/-) MEFs was rescued by IKKbeta(WT) but not IKKbeta(DeltaNBD), whereas neither IKKbeta(WT) nor IKKbeta(DeltaNBD) affected IL-1-induced NF-kappaB signaling. As previously described, classical NF-kappaB transcriptional activity was absent in IKKalpha(-/-) cells. Reconstitution with either IKKalpha(WT) or IKKalpha(DeltaNBD) rescued both IL-1 and TNF-induced transcription, demonstrating that NEMO association is not required for IKKalpha-dependent regulation of NF-kappaB-dependent transcription. Stably expressed IKKalpha(WT) or IKKbeta(WT) associated with endogenous IKKs and NEMO in IKKalpha(-/-) or IKKbeta(-/-) MEFs, respectively, resulting in formation of the heterotrimeric IKKalpha-IKKbeta-NEMO complex. In contrast, although the IKKalpha(DeltaNBD) and IKKbeta(DeltaNBD) mutants associated with endogenous IKKs containing an NBD, these dimeric endogenous IKK-IKK(DeltaNBD) complexes did not associate with NEMO. These findings therefore demonstrate that formation of the heterotrimeric IKKalpha-IKKbeta-NEMO holocomplex absolutely requires two intact NEMO-binding domains.
Figures
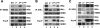
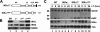
Similar articles
-
Interleukin-1-induced NF-kappaB activation is NEMO-dependent but does not require IKKbeta.J Biol Chem. 2007 Mar 23;282(12):8724-33. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M609613200. Epub 2007 Jan 23. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17244613 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of serine 68 in the IkappaB kinase (IKK)-binding domain of NEMO interferes with the structure of the IKK complex and tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activity.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jan 4;283(1):76-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M708856200. Epub 2007 Oct 31. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 17977820
-
IKKalpha and IKKbeta each function to regulate NF-kappaB activation in the TNF-induced/canonical pathway.PLoS One. 2010 Feb 25;5(2):e9428. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009428. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20195534 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
-
The IkappaB kinase complex: master regulator of NF-kappaB signaling.Immunol Res. 2008;42(1-3):3-18. doi: 10.1007/s12026-008-8025-1. Immunol Res. 2008. PMID: 18626576 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel insights into the cellular mechanisms of the anti-inflammatory effects of NF-kappaB essential modulator binding domain peptides.J Biol Chem. 2010 Apr 30;285(18):13498-506. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.099895. Epub 2010 Feb 18. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20167598 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperosmolarity invokes distinct anti-inflammatory mechanisms in pulmonary epithelial cells: evidence from signaling and transcription layers.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 5;9(12):e114129. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114129. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25479425 Free PMC article.
-
The IKK Kinases: Operators of Antiviral Signaling.Viruses. 2010 Jan;2(1):55-72. doi: 10.3390/v2010055. Epub 2010 Jan 8. Viruses. 2010. PMID: 21994600 Free PMC article.
-
Noncanonical NF-κB signaling is limited by classical NF-κB activity.Sci Signal. 2014 Feb 4;7(311):ra13. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2004557. Sci Signal. 2014. PMID: 24497610 Free PMC article.
-
The MC159 protein from the molluscum contagiosum poxvirus inhibits NF-κB activation by interacting with the IκB kinase complex.J Immunol. 2012 Mar 1;188(5):2371-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100136. Epub 2012 Feb 1. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22301546 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

