NEMO-binding domains of both IKKalpha and IKKbeta regulate IkappaB kinase complex assembly and classical NF-kappaB activation
- PMID: 19666475
- PMCID: PMC2785688
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.047563
NEMO-binding domains of both IKKalpha and IKKbeta regulate IkappaB kinase complex assembly and classical NF-kappaB activation
Abstract
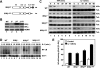
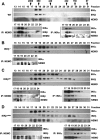
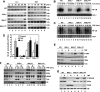
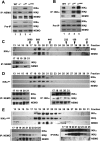
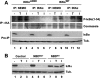
Proinflammatory NF-kappaB activation requires the IkappaB (inhibitor of NF-kappaB) kinase (IKK) complex that contains two catalytic subunits named IKKalpha and IKKbeta and a regulatory subunit named NF-kappaB essential modulator (NEMO). NEMO and IKKbeta are essential for tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-induced NF-kappaB activation, and we recently demonstrated that NEMO and IKKalpha are sufficient for interleukin (IL)-1-induced signaling. IKKalpha and IKKbeta both contain a functional NEMO-binding domain (NBD); however, the role of NEMO association with each kinase in NF-kappaB signaling and IKK complex formation remains unclear. To address this question, we stably reconstituted IKKalpha(-/-) and IKKbeta(-/-) murine embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) with wild-type (WT) or NBD-deficient (DeltaNBD) versions of IKKalpha and IKKbeta, respectively. TNF-induced classical NF-kappaB activation in IKKbeta(-/-) MEFs was rescued by IKKbeta(WT) but not IKKbeta(DeltaNBD), whereas neither IKKbeta(WT) nor IKKbeta(DeltaNBD) affected IL-1-induced NF-kappaB signaling. As previously described, classical NF-kappaB transcriptional activity was absent in IKKalpha(-/-) cells. Reconstitution with either IKKalpha(WT) or IKKalpha(DeltaNBD) rescued both IL-1 and TNF-induced transcription, demonstrating that NEMO association is not required for IKKalpha-dependent regulation of NF-kappaB-dependent transcription. Stably expressed IKKalpha(WT) or IKKbeta(WT) associated with endogenous IKKs and NEMO in IKKalpha(-/-) or IKKbeta(-/-) MEFs, respectively, resulting in formation of the heterotrimeric IKKalpha-IKKbeta-NEMO complex. In contrast, although the IKKalpha(DeltaNBD) and IKKbeta(DeltaNBD) mutants associated with endogenous IKKs containing an NBD, these dimeric endogenous IKK-IKK(DeltaNBD) complexes did not associate with NEMO. These findings therefore demonstrate that formation of the heterotrimeric IKKalpha-IKKbeta-NEMO holocomplex absolutely requires two intact NEMO-binding domains.
Figures
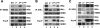
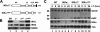
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

