Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells restore cardiac function in chronic ischemic cardiomyopathy via trilineage differentiating capacity
- PMID: 19666564
- PMCID: PMC2729013
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0903201106
Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells restore cardiac function in chronic ischemic cardiomyopathy via trilineage differentiating capacity
Abstract
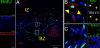
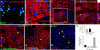
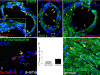
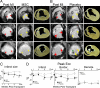
The mechanism(s) underlying cardiac reparative effects of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) remain highly controversial. Here we tested the hypothesis that MSCs regenerate chronically infarcted myocardium through mechanisms comprising long-term engraftment and trilineage differentiation. Twelve weeks after myocardial infarction, female swine received catheter-based transendocardial injections of either placebo (n = 4) or male allogeneic MSCs (200 million; n = 6). Animals underwent serial cardiac magnetic resonance imaging, and in vivo cell fate was determined by co-localization of Y-chromosome (Y(pos)) cells with markers of cardiac, vascular muscle, and endothelial lineages. MSCs engrafted in infarct and border zones and differentiated into cardiomyocytes as ascertained by co-localization with GATA-4, Nkx2.5, and alpha-sarcomeric actin. In addition, Y(pos) MSCs exhibited vascular smooth muscle and endothelial cell differentiation, contributing to large and small vessel formation. Infarct size was reduced from 19.3 +/- 1.7% to 13.9 +/- 2.0% (P < 0.001), and ejection fraction (EF) increased from 35.0 +/- 1.7% to 41.3 +/- 2.7% (P < 0.05) in MSC but not placebo pigs over 12 weeks. This was accompanied by increases in regional contractility and myocardial blood flow (MBF), particularly in the infarct border zone. Importantly, MSC engraftment correlated with functional recovery in contractility (R = 0.85, P < 0.05) and MBF (R = 0.76, P < 0.01). Together these findings demonstrate long-term MSC survival, engraftment, and trilineage differentiation following transplantation into chronically scarred myocardium. MSCs are an adult stem cell with the capacity for cardiomyogenesis and vasculogenesis which contribute, at least in part, to their ability to repair chronically scarred myocardium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
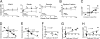
References
-
- Chien KR, Domian IJ, Parker KK. Cardiogenesis and the complex biology of regenerative cardiovascular medicine. Science. 2008;322:1494–1497. - PubMed
-
- Assmus B, et al. Transcoronary transplantation of progenitor cells after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1222–1232. - PubMed
-
- Meyer GP, et al. Intracoronary bone marrow cell transfer after myocardial infarction: Eighteen months' follow-up data from the randomized, controlled BOOST (bone marrow transfer to enhance ST-elevation infarct regeneration) trial. Circulation. 2006;113:1287–1294. - PubMed
-
- Psaltis PJ, Zannettino AC, Worthley SG, Gronthos S. Concise review: Mesenchymal stromal cells: Potential for cardiovascular repair. Stem Cells. 2008;26:2201–2210. - PubMed
-
- Belema-Bedada F, Uchida S, Martire A, Kostin S, Braun T. Efficient homing of multipotent adult mesenchymal stem cells depends on FROUNT-mediated clustering of CCR2. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;2:566–575. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

