Receptor guanylyl cyclases in Inka cells targeted by eclosion hormone
- PMID: 19666575
- PMCID: PMC2726410
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0812593106
Receptor guanylyl cyclases in Inka cells targeted by eclosion hormone
Abstract
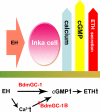
A signature of eclosion hormone (EH) action in insect ecdysis is elevation of cGMP in Inka cells, leading to massive release of ecdysis triggering hormone (ETH) and ecdysis initiation. Although this aspect of EH-induced signal transduction is well known, the receptor mediating this process has not been identified. Here, we describe a receptor guanylyl cyclase BdmGC-1 and its isoform BdmGC-1B in the Oriental fruit fly Bactrocera dorsalis that are activated by EH. The B form exhibits the conserved domains and putative N-glycosylation sites found in BdmGC-1, but possesses an additional 46-amino acid insertion in the extracellular domain and lacks the C-terminal tail of BdmGC-1. Combined immunolabeling and in situ hybridization reveal that BdmGC-1 is expressed in Inka cells. Heterologous expression of BdmGC-1 in HEK cells leads to robust increases in cGMP following exposure to low picomolar concentrations of EH. The B-isoform responds only to higher EH concentrations, suggesting different physiological roles of these cyclases. We propose that BdmGC-1 and BdmGC-1B are high- and low-affinity EH receptors, respectively.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A novel guanylyl cyclase receptor, BdmGC-1, is highly expressed during the development of the oriental fruit fly Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel).Insect Mol Biol. 2006 Feb;15(1):69-77. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2583.2006.00609.x. Insect Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16469070
-
Complex steroid-peptide-receptor cascade controls insect ecdysis.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2007 Aug-Sep;153(1-3):88-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2007.04.002. Epub 2007 Apr 11. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2007. PMID: 17507015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signal transduction in eclosion hormone-induced secretion of ecdysis-triggering hormone.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jul 6;276(27):25136-42. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M102421200. Epub 2001 Apr 19. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11313360
-
Molecular cloning and function of ecdysis-triggering hormones in the silkworm Bombyx mori.J Exp Biol. 2002 Nov;205(Pt 22):3459-73. doi: 10.1242/jeb.205.22.3459. J Exp Biol. 2002. PMID: 12364399
-
Molecular Physiology of Membrane Guanylyl Cyclase Receptors.Physiol Rev. 2016 Apr;96(2):751-804. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00022.2015. Physiol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27030537 Review.
Cited by
-
More than two decades of research on insect neuropeptide GPCRs: an overview.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2012 Nov 30;3:151. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2012.00151. eCollection 2012. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2012. PMID: 23226142 Free PMC article.
-
Acheron/Larp6 Is a Survival Protein That Protects Skeletal Muscle From Programmed Cell Death During Development.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jul 29;8:622. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00622. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32850788 Free PMC article.
-
Natriuretic peptides appeared after their receptors in vertebrates.BMC Evol Biol. 2019 Nov 26;19(1):215. doi: 10.1186/s12862-019-1517-x. BMC Evol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31771521 Free PMC article.
-
Secretory competence in a gateway endocrine cell conferred by the nuclear receptor βFTZ-F1 enables stage-specific ecdysone responses throughout development in Drosophila.Dev Biol. 2014 Jan 15;385(2):253-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.11.003. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24247008 Free PMC article.
-
The contribution of the genomes of a termite and a locust to our understanding of insect neuropeptides and neurohormones.Front Physiol. 2014 Nov 19;5:454. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00454. eCollection 2014. Front Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25477824 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Truman JW, Riddiford LM. Neuroendocrine control of ecdysis in silk moths. Science. 1970;167:1624–1626. - PubMed
-
- Kataoka H, Troetschler RG, Kramer SJ, Cesarin BJ, Schooley DA. Isolation and primary structure of the eclosion hormone of the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987;146:746–750. - PubMed
-
- Kono T, Nagasawa H, Isogai A, Fugo H, Suzuki A. Amino acid sequence of eclosion hormone of the silkworm Bombyx mori. Agr Biol Chem. 1987;51:2307–2308.
-
- Marti T, Takio K, Walsh KA, Terzi G, Truman JW. Microanalysis of the amino acid sequence of the eclosion hormone from the tobacco hornworm Manduca sexta. FEBS Lett. 1987;219:415–418. - PubMed
-
- Horodyski FM, Ewer J, Riddiford LM, Truman JW. Isolation, characterization and expression of the eclosion hormone gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Eur J Biochem. 1993;215:221–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

