Mechanism regulating proasthmatic effects of prolonged homologous beta2-adrenergic receptor desensitization in airway smooth muscle
- PMID: 19666775
- PMCID: PMC2770790
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00079.2009
Mechanism regulating proasthmatic effects of prolonged homologous beta2-adrenergic receptor desensitization in airway smooth muscle
Abstract
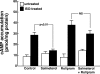
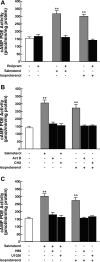
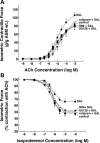
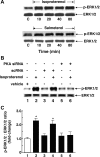
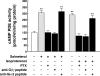
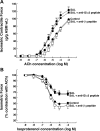
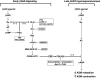
Use of long-acting beta(2)-adrenergic receptor (beta2AR) agonists to treat asthma incurs an increased risk of asthma morbidity with impaired bronchodilation and heightened bronchoconstriction, reflecting the adverse effects of prolonged homologous beta2AR desensitization on airway smooth muscle (ASM) function. Since phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) regulates ASM relaxation and contractility, we examined whether the changes in ASM function induced by prolonged homologous beta2AR desensitization are attributed to altered expression and action of PDE4. Cultured human ASM cells and isolated rabbit ASM tissues exposed for 24 h to the long-acting beta2AR agonist salmeterol exhibited impaired acute beta2AR-mediated cAMP accumulation and relaxation, respectively, together with ASM constrictor hyperresponsiveness. These proasthmatic-like changes in ASM function were associated with upregulated PDE4 activity due to enhanced expression of the PDE4D5 isoform and were prevented by pretreating the ASM preparations with the PDE4 inhibitor rolipram or with inhibitors of either PKA or ERK1/2 signaling. Extended studies using gene silencing and pharmacological approaches demonstrated that: 1) the mechanism underlying upregulated PDE4D5 expression following prolonged beta2AR agonist exposure involves PKA-dependent activation of G(i) protein signaling via its betagamma-subunits, which elicits downstream activation of ERK1/2 and its induction of PDE4D5 transcription; and 2) the induction of PDE4 activity and consequent changes in ASM responsiveness are prevented by pretreating the beta2AR agonist-exposed ASM preparations with inhibitors of G(i)-betagamma signaling. Collectively, these findings identify that the proasthmatic changes in ASM function resulting from prolonged homologous beta2AR desensitization are attributed to upregulated PDE4 expression induced by G(i)-betagamma-mediated cross-talk between the PKA and ERK1/2 signaling pathways.
Figures



References
-
- Beasley R, Pearce N, Crane J, Burgess C. Beta-agonists: what is the evidence that their use increases the risk of asthma morbidity and mortality? J Allergy Clin Immunol 104: S18–S30, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Billington CK, Le Jeune IR, Young KW, Hall IP. A major functional role for phosphodiesterase 4D5 in human airway smooth muscle cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 38: 1–7, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Bousquet-Melou A, Galitzky J, Moreno CM, Berlan M, Lafontan M. Desensitization of beta-adrenergic responses in adipocytes involves receptor subtypes and cAMP phosphodiesterase. Eur J Pharmacol 289: 235–247, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Chapman RW, House A, Jones H, Richard J, Celly C, Prelusky D, Ting P, Hunter JC, Lamca J, Phillips JE. Effect of inhaled roflumilast on the prevention and resolution of allergen-induced late phase airflow obstruction in Brown Norway rats. Eur J Pharmacol 571: 215–221, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Cheung D, Timmers MC, Zwinderman AH, Bel EH, Dijkman JH, Sterk PJ. Long-term effects of a long-acting beta 2-adrenoceptor agonist, salmeterol, on airway hyperresponsiveness in patients with mild asthma. N Engl J Med 327: 1198–1203, 1992 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

