Structural studies of soybean calmodulin isoform 4 bound to the calmodulin-binding domain of tobacco mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 provide insights into a sequential target binding mode
- PMID: 19667066
- PMCID: PMC2788880
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.025080
Structural studies of soybean calmodulin isoform 4 bound to the calmodulin-binding domain of tobacco mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 provide insights into a sequential target binding mode
Abstract
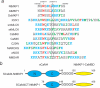
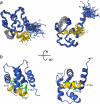
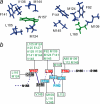
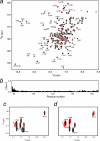
The calcium regulatory protein calmodulin (CaM) binds in a calcium-dependent manner to numerous target proteins. The calmodulin-binding domain (CaMBD) region of Nicotiana tabacum MAPK phosphatase has an amino acid sequence that does not resemble the CaMBD of any other known Ca(2+)-CaM-binding proteins. Using a unique fusion protein strategy, we have been able to obtain a high resolution solution structure of the complex of soybean Ca(2+)-CaM4 (SCaM4) and this CaMBD. Complete isotope labeling of both parts of the complex in the fusion protein greatly facilitated the structure determination by NMR. The 12-residue CaMBD region was found to bind exclusively to the C-lobe of SCaM4. A specific Trp and Leu side chain are utilized to facilitate strong binding through a novel "double anchor" motif. Moreover, the orientation of the helical peptide on the surface of Ca(2+)-SCaM4 is distinct from other known complexes. The N-lobe of Ca(2+)-SCaM4 in the complex remains free for additional interactions and could possibly act as a calcium-dependent adapter protein. Signaling through the MAPK pathway and increases in intracellular Ca(2+) are both hallmarks of the plant stress response, and our data support the notion that coordination of these responses may occur through the formation of a unique CaM-MAPK phosphatase multiprotein complex.
Figures
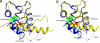
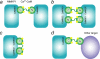
References
-
- Chin D., Means A. R. (2000) Trends Cell Biol. 10, 322–328 - PubMed
-
- Hoeflich K. P., Ikura M. (2002) Cell 108, 739–742 - PubMed
-
- Yamauchi E., Nakatsu T., Matsubara M., Kato H., Taniguchi H. (2003) Nat. Struct. Biol. 10, 226–231 - PubMed
-
- Maximciuc A. A., Putkey J. A., Shamoo Y., Mackenzie K. R. (2006) Structure 14, 1547–1556 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

