Phosphate-activated glutaminase-containing neurons in the rat paraventricular nucleus express angiotensin type 1 receptors
- PMID: 19667250
- PMCID: PMC2747100
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.134684
Phosphate-activated glutaminase-containing neurons in the rat paraventricular nucleus express angiotensin type 1 receptors
Abstract
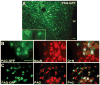
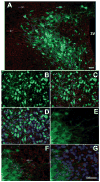
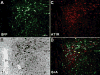
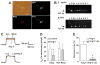
The centrally mediated cardiovascular regulatory actions of angiotensin II in normal and hypertensive rats include angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R)-mediated actions at the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) of the hypothalamus. Because the PVN consists of multiple neuronal populations, it is important to understand which neuronal types in the PVN are influenced by angiotensin II. Here we have developed a viral vector (Adeno-associated vector 2 [AAV2]-PAG-eGFP [PAG; phosphate-activated glutaminase promoter]) to drive expression of green fluorescent protein (GFP) primarily within glutamate neurons. At 10 to 14 days after bilateral microinjection (200 nL per side; 1.2 x10(12) genome copies) of AAV2-PAG-eGFP into adult Sprague-Dawley rat PVN, animals were euthanized and brains removed and used for isolation and culture of PVN neurons. Fluorescence microscopy and immunostaining using neuron and PAG-specific antibodies revealed the presence of GFP-containing glutamatergic neurons in these PVN cultures. Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings demonstrated that angiotensin II (100 nmol/L) produced a 16% decrease in delayed rectifier potassium current in approximately 50% of the GFP-containing neurons, an effect that was abolished by the AT1R antagonist losartan (1 mumol/L). Consistently, 9 of 28 GFP/PAG-expressing neurons contained AT1R mRNA, as indicated by single-cell RT-PCR. Furthermore, specific GFP/PAG-positive neurons in the PVN that project to the rostral ventrolateral medulla of the brain stem express immunoreactive AT1R. In conclusion, we have demonstrated the presence of functional AT1R on PAG-positive (largely glutamate) neurons within rat PVN, certain of which project to the rostral ventrolateral medulla.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Placental ischemia-upregulated angiotensin II type 1 receptor in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus contributes to hypertension in rat.Pflugers Arch. 2024 Nov;476(11):1677-1691. doi: 10.1007/s00424-024-03010-2. Epub 2024 Aug 31. Pflugers Arch. 2024. PMID: 39215834
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor modulates angiotensin signaling in the hypothalamus to increase blood pressure in rats.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 Mar 15;308(6):H612-22. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00776.2014. Epub 2015 Jan 9. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25576628 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II stimulates spinally projecting paraventricular neurons through presynaptic disinhibition.J Neurosci. 2003 Jun 15;23(12):5041-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-12-05041.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12832527 Free PMC article.
-
Adenoviral inhibition of AT1a receptors in the paraventricular nucleus inhibits acute increases in mean arterial blood pressure in the rat.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010 Nov;299(5):R1202-11. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00764.2009. Epub 2010 Aug 11. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20702798
-
Adaptive transcriptional dynamics of A2 neurons and central cardiovascular control pathways.Exp Physiol. 2012 Apr;97(4):462-8. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2011.059790. Epub 2011 Oct 14. Exp Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22002872 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroimmune communication in hypertension and obesity: a new therapeutic angle?Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Jun;138(3):428-40. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.02.005. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23458610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in the paraventricular nucleus plays a major role in the sympathoexcitatory response to salt.Hypertension. 2010 Nov;56(5):956-63. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.155101. Epub 2010 Oct 11. Hypertension. 2010. PMID: 20937969 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-10 inhibits angiotensin II-induced decrease in neuronal potassium current.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013 Apr 15;304(8):C801-7. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00398.2012. Epub 2013 Feb 20. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23426971 Free PMC article.
-
Brain microglial cytokines in neurogenic hypertension.Hypertension. 2010 Aug;56(2):297-303. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.150409. Epub 2010 Jun 14. Hypertension. 2010. PMID: 20547972 Free PMC article.
-
Activation AMPK in Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus Improves Renovascular Hypertension Through ERK1/2-NF-κB Pathway.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024 Sep;24(9):904-917. doi: 10.1007/s12012-024-09888-9. Epub 2024 Jul 15. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39008239
References
-
- Swanson LW, Sawchenko PE. Paraventricular nucleus: A site for the integration of neuroendocrine and autonomic mechanisms. Neuroendocrinology. 1980;31:410–417. - PubMed
-
- Allen AM. Inhibition of the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in spontaneously hypertensive rats dramatically reduces sympathetic vasomotor tone. Hypertension. 2002;39:275–280. - PubMed
-
- Stocker SD, Keith KJ, Toney GM. Acute inhibition of the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus decreases renal sympathetic nerve activity and arterial blood pressure in water-deprived rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2004;286:R719–725. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

