Antimalarial activity of simalikalactone E, a new quassinoid from Quassia amara L. (Simaroubaceae)
- PMID: 19667291
- PMCID: PMC2764154
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00951-09
Antimalarial activity of simalikalactone E, a new quassinoid from Quassia amara L. (Simaroubaceae)
Abstract
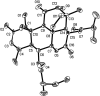
We report the isolation and identification of a new quassinoid named simalikalactone E (SkE), extracted from a widely used Amazonian antimalarial remedy made out of Quassia amara L. (Simaroubaceae) leaves. This new molecule inhibited the growth of Plasmodium falciparum cultured in vitro by 50%, in the concentration range from 24 to 68 nM, independently of the strain sensitivity to chloroquine. We also showed that this compound was able to decrease gametocytemia with a 50% inhibitory concentration sevenfold lower than that of primaquine. SkE was found to be less toxic than simalikalactone D (SkD), another antimalarial quassinoid from Q. amara, and its cytotoxicity on mammalian cells was dependent on the cell line, displaying a good selectivity index when tested on nontumorogenic cells. In vivo, SkE inhibited murine malaria growth of Plasmodium vinckei petteri by 50% at 1 and 0.5 mg/kg of body weight/day, by the oral or intraperitoneal routes, respectively. The contribution of quassinoids as a source of antimalarial molecules needs therefore to be reconsidered.
Figures
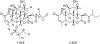


References
-
- Adesanwo, J. K., O. Ekundayo, F. O. Shode, V. C. O. Njar, A. J. J. van den Berge, and O. A. T. Oludahunsi. 2004. Eniotorin, an anti-malarial coumarin from the root bark of Quassia undulata. Niger. J. Nat. Prod. Med. 8:69-73.
-
- Arnot, D. E., and K. Gull. 1998. The Plasmodium cell cycle: facts and questions. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 92:361-365. - PubMed
-
- Bertani, S., G. Bourdy, I. Landau, J. C. Robinson, P. Esterre, and E. Deharo. 2005. Evaluation of French Guiana traditional antimalarial remedies. J. Ethnopharmacol. 98:45-54. - PubMed
-
- Bertani, S., E. Houël, G. Bourdy, D. Stien, V. Jullian, I. Landau, and E. Deharo. 2007. Quassia amara L. (Simaroubaceae) leaf tea: effect of the growing stage and desiccation status on the antimalarial activity of a traditional preparation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 111:40-42. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

