Alternatively spliced vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 is an essential endogenous inhibitor of lymphatic vessel growth
- PMID: 19668192
- PMCID: PMC2882165
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2018
Alternatively spliced vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 is an essential endogenous inhibitor of lymphatic vessel growth
Abstract
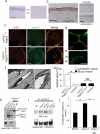
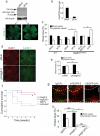
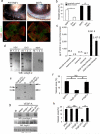
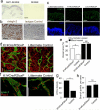
Disruption of the precise balance of positive and negative molecular regulators of blood and lymphatic vessel growth can lead to myriad diseases. Although dozens of natural inhibitors of hemangiogenesis have been identified, an endogenous selective inhibitor of lymphatic vessel growth has not to our knowledge been previously described. We report the existence of a splice variant of the gene encoding vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (Vegfr-2) that encodes a secreted form of the protein, designated soluble Vegfr-2 (sVegfr-2), that inhibits developmental and reparative lymphangiogenesis by blocking Vegf-c function. Tissue-specific loss of sVegfr-2 in mice induced, at birth, spontaneous lymphatic invasion of the normally alymphatic cornea and hyperplasia of skin lymphatics without affecting blood vasculature. Administration of sVegfr-2 inhibited lymphangiogenesis but not hemangiogenesis induced by corneal suture injury or transplantation, enhanced corneal allograft survival and suppressed lymphangioma cellular proliferation. Naturally occurring sVegfr-2 thus acts as a molecular uncoupler of blood and lymphatic vessels; modulation of sVegfr-2 might have therapeutic effects in treating lymphatic vascular malformations, transplantation rejection and, potentially, tumor lymphangiogenesis and lymphedema (pages 993-994).
Figures
Comment in
-
Blocking the path of lymphatic vessels.Nat Med. 2009 Sep;15(9):993-4. doi: 10.1038/nm0909-993. Nat Med. 2009. PMID: 19734869 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 is essential for corneal alymphaticity.Blood. 2013 May 16;121(20):4242-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-08-453043. Epub 2013 Mar 8. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23476047 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of lymphangiogenesis by soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 in a mouse lung cancer model.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Dec;84:660-665. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.09.083. Epub 2016 Sep 30. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27697638
-
Soluble VEGFR-2: an antilymphangiogenic variant of VEGF receptors.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Oct;1207 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):E7-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05714.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20961309 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphangiogenesis Guidance Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications in Pathological States of the Cornea.Cells. 2023 Jan 14;12(2):319. doi: 10.3390/cells12020319. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36672254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lymphangiogenic growth factors, receptors and therapies.Thromb Haemost. 2003 Aug;90(2):167-84. doi: 10.1160/TH03-04-0200. Thromb Haemost. 2003. PMID: 12888864 Review.
Cited by
-
Watching lymphatic vessels grow by making them glow.Cell Res. 2012 Jan;22(1):12-3. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.191. Epub 2011 Nov 29. Cell Res. 2012. PMID: 22124234 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Role of VEGF Receptors as Molecular Target in Nuclear Medicine for Cancer Diagnosis and Combination Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 3;13(5):1072. doi: 10.3390/cancers13051072. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33802353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuron-specific deletion of VEGF or its receptor Flk-1 occludes the antidepressant-like effects of desipramine and fluoxetine in mice.Neuropsychopharmacol Rep. 2024 Mar;44(1):246-249. doi: 10.1002/npr2.12393. Epub 2023 Nov 13. Neuropsychopharmacol Rep. 2024. PMID: 37960997 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Neuronal VEGF Signaling in the Prefrontal Cortex in the Rapid Antidepressant Effects of Ketamine.Am J Psychiatry. 2019 May 1;176(5):388-400. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2018.17121368. Epub 2019 Jan 4. Am J Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30606046 Free PMC article.
-
VEGFR-2 expression in carcinoid cancer cells and its role in tumor growth and metastasis.Int J Cancer. 2011 Mar 1;128(5):1045-56. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25441. Int J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 20473929 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferrara N, Kerbel RS. Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target. Nature. 2005;438:967–974. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature. 2005;438:932–936. - PubMed
-
- Fenwick A. Waterborne infectious diseases--could they be consigned to history? Science. 2006;313:1077–1081. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P, et al. Abnormal blood vessel development and lethality in embryos lacking a single Vegf allele. Nature. 1996;380:435–439. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N, et al. Heterozygous embryonic lethality induced by targeted inactivation of the Vegf gene. Nature. 1996;380:439–442. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- EY017182/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY015422/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY017182/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 EY020442/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY015422/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EY019778/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY018836/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY020672/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY017950/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY018350/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY018836/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY017950/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY018350/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

