The prolyl isomerase Pin1 regulates the NF-kappaB signaling pathway and interleukin-8 expression in glioblastoma
- PMID: 19668231
- PMCID: PMC5987556
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2009.232
The prolyl isomerase Pin1 regulates the NF-kappaB signaling pathway and interleukin-8 expression in glioblastoma
Abstract
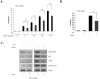
The brain tumor glioblastoma (GBM) remains one of the most aggressive and devastating tumors despite decades of effort to find more effective treatments. A hallmark of GBM is the constitutive activation of the nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-kappaB) signaling pathway, which regulates cell proliferation, inflammation, migration and apoptosis. The prolyl isomerase, Pin1, has been found to bind directly to the NF-kappaB protein, p65, and cause increases in NF-kappaB promoter activity in a breast cancer model. We now present evidence that this interaction occurs in GBM and that it has important consequences on NF-kappaB signaling. We demonstrate that Pin1 levels are enhanced in primary GBM tissues compared with controls, and that this difference in Pin1 expression affects the migratory capacity of GBM-derived cells. Pin1 knockdown decreases the amount of activated, phosphorylated p65 in the nucleus, resulting in inhibition of the transcriptional program of the IL-8 gene. Through the use of microarray, we also observed changes in the expression levels of other NF-kappaB regulated genes due to Pin1 knockdown. Taken together, these data suggest that Pin1 is an important regulator of NF-kappaB in GBM, and support the notion of using Pin1 as a therapeutic target in the future.
Figures

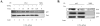



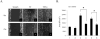
References
-
- Aggarwal BB. Nuclear factor-kappaB: the enemy within. Cancer Cell. 2004;6:203–8. - PubMed
-
- Ayala G, Wang D, Wulf G, Frolov A, Li R, Sowadski J, et al. The prolyl isomerase Pin1 is a novel prognostic marker in human prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2003;63:6244–51. - PubMed
-
- Bharti AC, Aggarwal BB. Nuclear factor-kappa B and cancer: its role in prevention and therapy. Biochem Pharmacol. 2002;64:883–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

