Single-molecule sequencing of an individual human genome
- PMID: 19668243
- PMCID: PMC4117198
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt.1561
Single-molecule sequencing of an individual human genome
Abstract
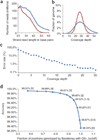
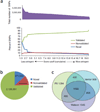
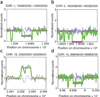
Recent advances in high-throughput DNA sequencing technologies have enabled order-of-magnitude improvements in both cost and throughput. Here we report the use of single-molecule methods to sequence an individual human genome. We aligned billions of 24- to 70-bp reads (32 bp average) to approximately 90% of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) reference genome, with 28x average coverage. Our results were obtained on one sequencing instrument by a single operator with four data collection runs. Single-molecule sequencing enabled analysis of human genomic information without the need for cloning, amplification or ligation. We determined approximately 2.8 million single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) with a false-positive rate of less than 1% as validated by Sanger sequencing and 99.8% concordance with SNP genotyping arrays. We identified 752 regions of copy number variation by analyzing coverage depth alone and validated 27 of these using digital PCR. This milestone should allow widespread application of genome sequencing to many aspects of genetics and human health, including personal genomics.
Figures
Comment in
-
DNA confidential.Nat Biotechnol. 2009 Sep;27(9):777. doi: 10.1038/nbt0909-777. Nat Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19741610
References
-
- Venter JC, et al. The sequence of the human genome. Science. 2001;291:1304–1351. - PubMed
-
- Lander ES, et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature. 2001;409:860–921. - PubMed
-
- Wheeler DA, et al. The complete genome of an individual by massively parallel DNA sequencing. Nature. 2008;452:872–876. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

