Gene expression in skeletal muscle biopsies from people with type 2 diabetes and relatives: differential regulation of insulin signaling pathways
- PMID: 19668377
- PMCID: PMC2719801
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006575
Gene expression in skeletal muscle biopsies from people with type 2 diabetes and relatives: differential regulation of insulin signaling pathways
Abstract
Background: Gene expression alterations have previously been associated with type 2 diabetes, however whether these changes are primary causes or secondary effects of type 2 diabetes is not known. As healthy first degree relatives of people with type 2 diabetes have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, they provide a good model in the search for primary causes of the disease.
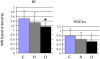
Methods/principal findings: We determined gene expression profiles in skeletal muscle biopsies from Caucasian males with type 2 diabetes, healthy first degree relatives, and healthy controls. Gene expression was measured using Affymetrix Human Genome U133 Plus 2.0 Arrays covering the entire human genome. These arrays have not previously been used for this type of study. We show for the first time that genes involved in insulin signaling are significantly upregulated in first degree relatives and significantly downregulated in people with type 2 diabetes. On the individual gene level, 11 genes showed altered expression levels in first degree relatives compared to controls, among others KIF1B and GDF8 (myostatin). LDHB was found to have a decreased expression in both groups compared to controls.
Conclusions/significance: We hypothesize that increased expression of insulin signaling molecules in first degree relatives of people with type 2 diabetes, work in concert with increased levels of insulin as a compensatory mechanism, counter-acting otherwise reduced insulin signaling activity, protecting these individuals from severe insulin resistance. This compensation is lost in people with type 2 diabetes where expression of insulin signaling molecules is reduced.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Insulin signal transduction in skeletal muscle from glucose-intolerant relatives of type 2 diabetic patients [corrected].Diabetes. 2001 Dec;50(12):2770-8. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.50.12.2770. Diabetes. 2001. PMID: 11723060
-
GLUT4 and UBC9 protein expression is reduced in muscle from type 2 diabetic patients with severe insulin resistance.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27854. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027854. Epub 2011 Nov 16. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22114711 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression profile in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetes and the effect of insulin treatment.Diabetes. 2002 Jun;51(6):1913-20. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.51.6.1913. Diabetes. 2002. PMID: 12031981 Clinical Trial.
-
Metabolism and insulin signaling in common metabolic disorders and inherited insulin resistance.Dan Med J. 2014 Jul;61(7):B4890. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 25123125 Review.
-
From receptor to effector: insulin signal transduction in skeletal muscle from type II diabetic patients.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002 Jun;967:120-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04270.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002. PMID: 12079842 Review.
Cited by
-
Myostatin inhibition prevents diabetes and hyperphagia in a mouse model of lipodystrophy.Diabetes. 2012 Oct;61(10):2414-23. doi: 10.2337/db11-0915. Epub 2012 May 17. Diabetes. 2012. PMID: 22596054 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Dietary Supplements, Nutraceutical Agents, and Physical Exercise on Myostatin Levels: Hope or Hype?Metabolites. 2022 Nov 20;12(11):1146. doi: 10.3390/metabo12111146. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36422286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of phosphofructokinase in skeletal muscle is influenced by genetic variation and associated with insulin sensitivity.Diabetes. 2014 Mar;63(3):1154-65. doi: 10.2337/db13-1301. Epub 2013 Dec 4. Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 24306210 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose tolerance is associated with differential expression of microRNAs in skeletal muscle: results from studies of twins with and without type 2 diabetes.Diabetologia. 2015 Feb;58(2):363-73. doi: 10.1007/s00125-014-3434-2. Epub 2014 Nov 19. Diabetologia. 2015. PMID: 25403480 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide screening for genetic variants in polyadenylation signal (PAS) sites in mouse selection lines for fatness and leanness.Mamm Genome. 2023 Mar;34(1):12-31. doi: 10.1007/s00335-022-09967-8. Epub 2022 Nov 21. Mamm Genome. 2023. PMID: 36414820 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Elbein SC. Genetics of type 2 diabetes: an overview for the millennium. Diabetes technology & therapeutics. 2000;2:391–400. - PubMed
-
- Jackson S, Bagstaff SM, Lynn S, Yeaman SJ, Turnbull DM, et al. Decreased insulin responsiveness of glucose uptake in cultured human skeletal muscle cells from insulin-resistant nondiabetic relatives of type 2 diabetic families. Diabetes. 2000;49:1169–1177. - PubMed
-
- Hansen L, Gaster M, Oakeley EJ, Brusgaard K, Damsgaard-Nielsen EM, et al. Expression profiling of insulin action in human myotubes: induction of inflammatory and pro-angiogenic pathways in relationship with glycogen synthesis and type 2 diabetes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;323:685–695. - PubMed
-
- Jafar-Mohammadi B, McCarthy M. Genetics of type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity - a review. Ann Med1-9 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

