Analgesic and anti-inflammatory effectiveness of nepafenac 0.1% for cataract surgery
- PMID: 19668532
- PMCID: PMC2704522
Analgesic and anti-inflammatory effectiveness of nepafenac 0.1% for cataract surgery
Abstract
Background: To compare nepafenac 0.1% with placebo and ketorolac 0.5% for prevention and treatment of ocular pain and inflammation after cataract surgery.
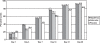
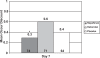
Methods: In a multi-center, randomized, placebo- and active-controlled, double-masked clinical trial, 227 patients with cataract were randomized to receive nepafenac 0.1%, ketorolac 0.5%, or placebo TID beginning 1 day pre-operatively and continuing for 21 days postoperatively. At each postoperative visit, cure rates and clinical success rates (</=5 aqueous cells and no flare) were calculated, and investigators evaluated patients' pain. On Day 7, patients judged ocular comfort after study drug instillation.
Results: Nepafenac 0.1% produced significantly more cures compared to placebo at Day 14 (76.3% vs 59.2%, p = 0.0241), more clinical successes from Day 7 onward (p < 0.05), and more pain-free patients from Day 3 onward (p < 0.05). Nepafenac 0.1% was superior to ketorolac 0.5% in terms of clinical success at Day 14 (p = 0.0319) and in percentage of pain-free patients at Day 3 (p = 0.0366). Nepafenac 0.1% also demonstrated less discomfort upon instillation than ketorolac 0.5% (p = 0.0158).
Conclusion: The anti-inflammatory efficacy of nepafenac 0.1% is better than that of placebo; it is also more comfortable and at least equal to ketorolac 0.5% in the prevention and treatment of postoperative ocular pain and inflammation.
Keywords: NSAIDs; cataract; inflammation; ketorolac; nepafenac.
Figures

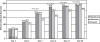
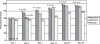
References
-
- ACULAR® [package insert] Palo Alto, CA: Allergan, Inc; 2002.
-
- ACULAR LS® [package insert] Palo Alto, CA: Allergan, Inc; 2003.
-
- Bodaghi B, Weber ME, Arnoux YV, et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of two formulations of diclofenac sodium 0.1% eyedrops in controlling postoperative inflammation after cataract surgery. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2005;15:702–11. - PubMed
-
- Brennan KM, Brown RM, Roberts CW. A comparison of topical non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to steroids for control of post cataract inflammation. J Am Soc Ophthalmic Reg Nurses. 1993;XVIII:8–11. - PubMed
-
- Colin J, Paquette B. Comparison of the analgesic efficacy and safety of nepafenac ophthalmic suspension compared with diclofenac ophthalmic solution for ocular pain and photophobia after excimer laser surgery: a phase ii, randomized, double-masked trial. Clin Ther. 2006;28:527–36. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

