Inhibition of surgically induced miosis and prevention of postoperative macular edema with nepafenac
- PMID: 19668569
- PMCID: PMC2708994
- DOI: 10.2147/opth.s4820
Inhibition of surgically induced miosis and prevention of postoperative macular edema with nepafenac
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effectiveness of prophylactic administration of nepafenac 0.1% in maintaining mydriasis and in preventing postoperative macular edema following cataract surgery.
Methods: This was a prospective, randomized, single-masked comparative study in 60 patients undergoing phacoemulsification cataract surgery. Patients were randomized to either the nepafenac or the control group. Nepafenac was administered 3 times daily 1 day before surgery and continued for 6 weeks. The control group received tobramycin-dexamethasone treatment only. Trans-operative mydriasis was measured before surgery, after nuclear emulsification, following cortex aspiration, and at the conclusion of surgery. Macular optical coherence tomography determined central foveal thickness (FT) and total macular volume (TMV) before surgery and at 2 and 6 weeks after surgery. All patients received tobramycin-dexamethasone for 2 weeks after surgery.
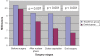
Results: The difference in mean pupil size, at the end of surgery, between the control group (6.84 +/- 0.93 mm) and the nepafenac group (7.91 +/- 0.74 mm) was statistically significant (p < 0.001). There were no significant differences in FT values between the two groups at any time point; however, TMV at 2 and at 6 weeks was statistically significantly different (p < 0.001), with higher TMV in the control group.
Conclusion: Prophylactic use of nepafenac was effective in reducing macular edema after cataract surgery and in maintaining trans-operative mydriasis.
Keywords: cataract surgery; macular edema; mydriasis; nepafenac; prophylactic.
Figures
References
-
- Linebarger EJ, Hardten DR, Shah GK, et al. Phacoemulsification and modern cataract surgery. Surv Ophthalmol. 1999;44:123–147. - PubMed
-
- Gogate PM, Kulkarni SR, Krishnaiah S, et al. Safety and efficacy of phacoemulsification compared with manual small-incision cataract surgery by a randomized controlled clinical trial: six-week results. Ophthalmology. 2005;112:869–874. - PubMed
-
- Mohammadpour M, Jafarinasab MR, Javadi MA. Outcomes of acute postoperative inflammation after cataract surgery. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2007;17:20–28. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources