Contemporary aspects in the prognosis of traumatic hyphemas
- PMID: 19668580
- PMCID: PMC2709009
- DOI: 10.2147/opth.s5399
Contemporary aspects in the prognosis of traumatic hyphemas
Abstract
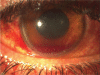
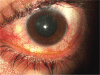
Purpose: The present study concerns traumatic hyphemas and their prognostic factors and signs. The aim of this study is to determine the prognostic factors and signs of traumatic hyphemas.
Methods: During the last five years, 72 young individuals were hospitalized with the diagnosis of suffering a traumatic hyphema and were divided in three groups according to the extent of their hyphema. The first group concerns 38 patients with a small hyphema 3-4 mm, the second group concerns 22 patients with moderate hyphema reaching the pupillary border, and the third group concerns 12 patients with a total hyphema.
Results: The hyphema was absorbed in 63 patients and the IOP was controlled with medical treatment after 3-24 days. However, surgical management was necessary for two patients. Finally, antiglaucomatous treatment was administered in seven patients with persistent high intraocular pressure.
Conclusions: The important clinical signs that determine the prognosis of such hyphemas are the size of hyphema, the blood color, recurrent hemorrhage, the absorption time, the increase of intraocular pressure, and blood staining of the cornea.
Keywords: IOP rise; blood staining of the cornea; prognostic signs; traumatic hyphema.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Traumatic hyphema: surgical vs medical management.Ann Ophthalmol. 1975 May;7(5):659-62, 664-6, 668-70. Ann Ophthalmol. 1975. PMID: 1137285 Clinical Trial.
-
Outcome of traumatic hyphema.Ann Ophthalmol. 1975 May;7(5):701-6. Ann Ophthalmol. 1975. PMID: 1137287
-
Traumatic hyphema.J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1986 Mar-Apr;23(2):95-7. doi: 10.3928/0191-3913-19860301-12. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1986. PMID: 3958878
-
Management of traumatic hyphema.Surv Ophthalmol. 2002 Jul-Aug;47(4):297-334. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6257(02)00317-x. Surv Ophthalmol. 2002. PMID: 12161209 Review.
-
Hyphema: diagnosis and management.Retina. 1990;10 Suppl 1:S65-71. doi: 10.1097/00006982-199010001-00011. Retina. 1990. PMID: 2191385 Review.
Cited by
-
Paracentesis as surgical intervention in traumatic hyphaema: opinions and practices of nigerian ophthalmologists.Ophthalmol Eye Dis. 2012 Aug 30;4:71-8. doi: 10.4137/OED.S9411. Print 2012. Ophthalmol Eye Dis. 2012. PMID: 23650459 Free PMC article.
-
A rare mode of golf related eye injury: Freak accidents do occur!Med J Armed Forces India. 2014 Apr;70(2):192-4. doi: 10.1016/j.mjafi.2013.02.007. Epub 2013 May 10. Med J Armed Forces India. 2014. PMID: 24843211 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
An office-based procedure for hyphema treatment.Case Rep Ophthalmol Med. 2015;2015:321076. doi: 10.1155/2015/321076. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Case Rep Ophthalmol Med. 2015. PMID: 25866691 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Walton W, Von Hagen S, Grigorian R, Zarbin M. Management of traumatic hyphema. Surv Ophthalmol. 2002;47(4):297–334. - PubMed
-
- Brandt MT, Haug RH. Traumatic hyphema: a comprehensive review. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2001;59(12):1462–1470. - PubMed
-
- Edward WC, Layden WE. Traumatic hyphema. A report of 184 consecutive cases. Am J Ophthalmol. 1973;75(1):110–116. - PubMed
-
- Shingleton BJ, Hersh PS, Kenyon KR, editors. Eye Trauma. St. Louis, MO: Mosby; 1991. pp. 104–116.
-
- Witteman GJ, Brubaker SJ, Johnson M, Marks RG. The incidence of rebleeding in traumatic hyphema. Ann Ophthalmol. 1985;17(9):525–526. 528–529. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources