Quantitative determination of glycosaminoglycans in tears of diabetic patients
- PMID: 19668757
- PMCID: PMC2694000
- DOI: 10.2147/opth.s2643
Quantitative determination of glycosaminoglycans in tears of diabetic patients
Abstract
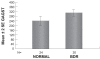
Purpose: To determine the amount of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) in tears of patients with diabetic retinopathy (DR) and to compare it with normal subjects.
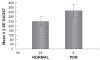
Methods: 38 patients with DR and 24 normal volunteers were included. Thirty subjects suffered from background diabetic retinopathy (BDR) and 8 from proliferate diabetic retinopathy (PDR). For the GAGs assay, the uronic carbazole reaction was used.
Results: The mean concentration of GAGs was significantly higher in patients with DR than in normal subjects. The GAGs concentration in patients with BDR or PDR was significantly higher than in normal subjects.
Conclusion: The measurement of GAGs in tears of diabetic patients could be a tool in order to assess the stability or not of the disease.
Keywords: diabetic retinopathy; glycosaminoglycans; tears.
Figures
References
-
- Bitter T, Muir HM. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Annal Biochem. 1962;4:330–4. - PubMed
-
- Ceriello A, Giungliano D, Dello Russo P, et al. Glycosaminoglycans in human diabetes. Diabetes Metabol. 1983;9:32–4. - PubMed
-
- Deckert T, Kofoed Enevoldsen A, Vidal P, et al. Size- and charge selectivity of glomerular filtration in Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients with and without albuminuria. Diabetologia. 1993;36:244–51. - PubMed
-
- Gambero G, Cicerello E, Mastrosimone S, et al. High urinary excretion of glycosaminoglycans; a possible marker of glomerular involvement in diabetes. Metabolism. 1989;38:419–20. - PubMed
-
- Hansen C, Aichner C, Otto E, et al. Abberant distribution and increased urinary glycosaminoglycans excretion in type II diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) Exp Clin Endocrinol Diab. 1996;104:145–9.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources