L-Arginine stimulates proliferation and prevents endotoxin-induced death of intestinal cells
- PMID: 19669080
- PMCID: PMC2850530
- DOI: 10.1007/s00726-009-0334-8
L-Arginine stimulates proliferation and prevents endotoxin-induced death of intestinal cells
Abstract
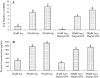
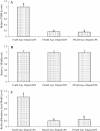
This study tested the hypothesis that L-arginine (Arg) may stimulate cell proliferation and prevent lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced death of intestinal cells. Intestinal porcine epithelial cells (IPEC-1) were cultured for 4 days in Arg-free Dulbecco's modified Eagle's-F12 Ham medium (DMEM-F12) containing 10, 100 or 350 microM Arg and 0 or 20 ng/ml LPS. Cell numbers, protein concentrations, protein synthesis and degradation, as well as mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling pathways were determined. Without LPS, IPEC-1 cells exhibited time- and Arg-dependent growth curves. LPS treatment increased cell death and reduced protein concentrations in IPEC-1 cells. Addition of 100 and 350 microM Arg to culture medium dose-dependently attenuated LPS-induced cell death and reduction of protein concentrations, in comparison with the basal medium containing 10 microM Arg. Furthermore, supplementation of 100 and 350 microM Arg increased protein synthesis and reduced protein degradation in both control and LPS-treated IPEC-1 cells. Consistent with the data on cell growth and protein turnover, addition of 100 or 350 microM Arg to culture medium increased relative protein levels for phosphorylated mTOR and phosphorylated ribosomal protein S6 kinase-1, while reducing the relative levels of TLR4 and phosphorylated levels of nuclear factor-kappaB in LPS-treated IPEC-1 cells. These results demonstrate a protective effect of Arg against LPS-induced enterocyte damage through mechanisms involving mTOR and TLR4 signaling pathways, as well as intracellular protein turnover.
Figures




Similar articles
-
L-Arginine stimulates the mTOR signaling pathway and protein synthesis in porcine trophectoderm cells.J Nutr Biochem. 2012 Sep;23(9):1178-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2011.06.012. Epub 2011 Dec 1. J Nutr Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22137265
-
L-arginine upregulates the gene expression of target of rapamycin signaling pathway and stimulates protein synthesis in chicken intestinal epithelial cells.Poult Sci. 2015 May;94(5):1043-51. doi: 10.3382/ps/pev051. Epub 2015 Mar 14. Poult Sci. 2015. PMID: 25771531
-
L-Glutamine or L-alanyl-L-glutamine prevents oxidant- or endotoxin-induced death of neonatal enterocytes.Amino Acids. 2009 May;37(1):131-42. doi: 10.1007/s00726-009-0243-x. Epub 2009 Feb 3. Amino Acids. 2009. PMID: 19189199
-
Alpha-ketoglutarate inhibits glutamine degradation and enhances protein synthesis in intestinal porcine epithelial cells.Amino Acids. 2012 Jun;42(6):2491-500. doi: 10.1007/s00726-011-1060-6. Epub 2011 Aug 23. Amino Acids. 2012. PMID: 21861169
-
Arginine-induced stimulation of protein synthesis and survival in IPEC-J2 cells is mediated by mTOR but not nitric oxide.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Dec;299(6):E899-909. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00068.2010. Epub 2010 Sep 14. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 20841502
Cited by
-
Effect of dietary arginine supplementation on reproductive performance of mice with porcine circovirus type 2 infection.Amino Acids. 2012 Jun;42(6):2089-94. doi: 10.1007/s00726-011-0942-y. Epub 2011 May 27. Amino Acids. 2012. PMID: 21617969 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary glutamate supplementation ameliorates mycotoxin-induced abnormalities in the intestinal structure and expression of amino acid transporters in young pigs.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 18;9(11):e112357. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112357. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25405987 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond protein synthesis: the emerging role of arginine in poultry nutrition and host-microbe interactions.Front Physiol. 2024 Jan 3;14:1326809. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1326809. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38235383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction mechanism of Trp-Arg dipeptide with calf thymus DNA.J Fluoresc. 2013 Sep;23(5):921-7. doi: 10.1007/s10895-013-1217-7. Epub 2013 Apr 20. J Fluoresc. 2013. PMID: 23604815
-
Effects of dietary arginine in ameliorating the deleterious effects induced by mycotoxins on growth, immune system, body organs in growing pigs.J Anim Sci Technol. 2022 Jul;64(4):727-739. doi: 10.5187/jast.2022.e54. Epub 2022 Jul 31. J Anim Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 35969699 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Austenaa LM, Carisen H, Hollung K et al (2008) Retinoic acid dampens LPS-induced NF-kB activity. J Nutr Biochem. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2008.07.002 - PubMed
-
- Ban H, Shigemitsu K, Yamatsuji T, et al. Arginine and leucine regulate p70S6 kinase and 4E-BP1 in intestinal epithelial cells. Int J Mol Med. 2004;13:537–543. - PubMed
-
- Corl BA, Odle J, Niu X, et al. Arginine activates intestinal p70(S6 k) and protein synthesis in piglet rotavirus enteritis. J Nutr. 2008;138:24–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

