A randomized controlled trial of thymalfasin plus transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 19669251
- PMCID: PMC2748379
- DOI: 10.1007/s12072-009-9132-3
A randomized controlled trial of thymalfasin plus transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: Patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) have few treatment options. Thymalfasin (thymosin α-1) is an immunomodulator that may increase response to ablative therapy through direct anti-tumor action or enhanced protection against infections. We compared transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) plus thymalfasin with TACE alone for unresectable HCC.
Methods: In this phase II, randomized trial, 25 patients received either TACE plus thymalfasin (1.6 mg SC, 5 times weekly; n = 14) or TACE alone (n = 11) for 24 weeks. Response was defined as transition to transplant eligibility or lack of disease progression through week 72. Survival was assessed through 24 months post-treatment.
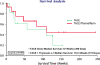
Results: Eight of fourteen (57.1%) patients in the TACE + thymalfasin group versus 5 of 11 (45.5%) patients in the TACE-only group became responders (P = 1.0). Four of fourteen TACE + thymalfasin patients versus none of 11 TACE-only patients became eligible for transplant. Median overall survival time was 110.3 weeks for the TACE + thymalfasin group versus 57.0 weeks for the TACE-only group (P = 0.45). Seven patients in each group experienced serious adverse events; there were no bacterial infections in the TACE + thymalfasin group versus 4 in the TACE-only group. There were 3 deaths in the TACE + thymalfasin group and 5 in the TACE-only group.
Conclusions: In patients with unresectable HCC, TACE + thymalfasin resulted in numerically higher rates of survival and tumor response, including transplant candidacy, with fewer bacterial infections, than TACE alone. Treatment regimens for HCC including thymalfasin as an immunomodulator should be evaluated in larger trials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of Drug-Eluting Beads Transarterial Chemoembolization Plus Camrelizumab Compared With Conventional Transarterial Chemoembolization Plus Camrelizumab for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancer Control. 2022 Jan-Dec;29:10732748221076806. doi: 10.1177/10732748221076806. Cancer Control. 2022. PMID: 35343254 Free PMC article.
-
Transarterial chemoembolization plus lenvatinib versus transarterial chemoembolization plus sorafenib as first-line treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: A prospective randomized study.Cancer. 2021 Oct 15;127(20):3782-3793. doi: 10.1002/cncr.33677. Epub 2021 Jul 8. Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34237154 Clinical Trial.
-
Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Plus Sorafenib Compared to TACE Alone in Transplant Recipients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Institution Experience.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 27;14(3):650. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030650. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35158918 Free PMC article.
-
Lenvatinib plus transarterial chemoembolization with or without immune checkpoint inhibitors for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A review.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 28;12:980214. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.980214. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36249023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transarterial chemoembolization combined with lenvatinib versus transarterial chemoembolization combined with sorafenib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2023 Feb 23;13:1074793. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1074793. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36910612 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prothymosin alpha: a ubiquitous polypeptide with potential use in cancer diagnosis and therapy.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2012 May;61(5):599-614. doi: 10.1007/s00262-012-1222-8. Epub 2012 Feb 26. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2012. PMID: 22366887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Status Quo and Development of Immunotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 May;54(3):692-698. doi: 10.12182/20230560108. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 37248607 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Recent advances and applications of peptide-agent conjugates for targeting tumor cells.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Nov;149(16):15249-15273. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05144-9. Epub 2023 Aug 15. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37581648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: expert consensus statement.HPB (Oxford). 2010 Jun;12(5):302-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2010.00182.x. HPB (Oxford). 2010. PMID: 20590903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Reappraisal of Thymosin Alpha1 in Cancer Therapy.Front Oncol. 2019 Sep 6;9:873. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00873. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31555601 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kim WR, Gores GJ, Benson JT, Therneau TM, Melton LJ., III Mortality and hospital utilization for hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:486–493. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous