Identifying complex brain networks using penalized regression methods
- PMID: 19669480
- PMCID: PMC2585631
- DOI: 10.1007/s10867-008-9077-0
Identifying complex brain networks using penalized regression methods
Abstract
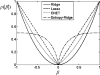
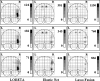
The recorded electrical activity of complex brain networks through the EEG reflects their intrinsic spatial, temporal and spectral properties. In this work we study the application of new penalized regression methods to i) the spatial characterization of the brain networks associated with the identification of faces and ii) the PARAFAC analysis of resting-state EEG. The use of appropriate constraints through non-convex penalties allowed three types of inverse solutions (Loreta, Lasso Fusion and ENet L) to spatially localize networks in agreement with previous studies with fMRI. Furthermore, we propose a new penalty based in the Information Entropy for the constrained PARAFAC analysis of resting EEG that allowed the identification in time, frequency and space of those brain networks with minimum spectral entropy. This study is an initial attempt to explicitly include complexity descriptors as a constraint in multilinear EEG analysis.
Figures


References
-
- None
- Pascual-Marqui, R.D.: Review of methods for solving the EEG inverse problem. Int. J. Bioelectromagn. 1, (1), 75–86 (1999)
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1109/51.956819', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1109/51.956819'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '11668896', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11668896/'}]}
- Durka, P.J., Blinowska, K.J.: A unified time–frequency parametrization of EEG. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. 20, (5), 47–53 (2001) - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1126/science.1066168', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1066168'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '11809976', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11809976/'}]}
- Makeig, S., Westerfield, M., Jung, T.P., Enghoff, S., Townsend, J., Courchesne, E., Sejnowski, T.J.: Dynamic brain sources of visual evoked responses. Science 295, 690–694 (2002) - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.03.039', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.03.039'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15219576', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15219576/'}]}
- Miwakeichi, F., Martínez-Montes, E., Valdés-Sosa, P.A., Nishiyama, N., Mizuhara, H., Yamaguchi, Y.: Decomposing EEG data into space–time–frequency components using Parallel Factor Analysis. Neuroimage 22, (3), 1035–1045 (2004) - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S1053-8119(03)00160-5', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s1053-8119(03)00160-5'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12948704', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12948704/'}]}
- Harrison, L., Penny, W.D., Friston, K.: Multivariate autoregressive modeling of fmri time series. Neuroimage 19, 1477–1491 (2003) - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

