Phase I trial of continuous infusion anti-mesothelin recombinant immunotoxin SS1P
- PMID: 19671873
- PMCID: PMC2754261
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0062
Phase I trial of continuous infusion anti-mesothelin recombinant immunotoxin SS1P
Abstract
Purpose: To conduct a phase I trial of recombinant immunotoxin SS1P given by continuous infusion in chemoresistant solid tumors expressing mesothelin.
Experimental design: Eligible patients had mesothelioma, ovarian, or pancreatic cancer, which was recurrent or unresectable despite standard therapy, and were mesothelin positive by immunohistochemistry. SS1P was given by continuous infusion for 10 days, and cycles could be repeated at 4-week intervals in the absence of neutralizing antibodies or progressive disease.
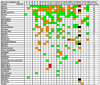
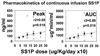
Results: Twenty-four patients, five with peritoneal mesothelioma, nine with pleural mesothelioma, two with pleural-peritoneal mesothelioma, seven with ovarian carcinoma, and one with pancreatic carcinoma, received 4, 8, 12, 18, and 25 microg/kg/d x10. The maximum tolerated dose was 25 microg/kg/d x10, where one of six patients had dose-limiting toxicity due to reversible vascular leak syndrome. Immunogenicity was observed in 18 (75%) of 24 patients, and five (21%) received a second cycle. Constant plasma levels of SS1P were maintained for most of the 10-day infusion time, with median peak levels of up to 153 ng/mL. One patient had a partial response. Nonmajor responses included cessation of ascites and independence from paracentesis, resolution of masses by positron emission tomography, and improved pain and range of motion.
Conclusions: As a single agent by continuous infusion, recombinant immunotoxin SS1P was well tolerated up to 25 microg/kg/d x10 and showed evidence of modest clinical activity. Continuous infusion showed no significant advantage over bolus dosing, and further clinical development of SS1P is proceeding by bolus dosing in combination with chemotherapy.
Figures
References
-
- Palumbo C, Bei R, Procopio A, Modesti A. Molecular targets and targeted therapies for malignant mesothelioma. Curr Med Chem. 2008;15:855–867. - PubMed
-
- Hassan R, Bera T, Pastan I. Mesothelin: a new target for immunotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:3937–3942. - PubMed
-
- Chang K, Pai LH, Pass H, et al. Monoclonal antibody K1 reacts with epithelial mesothelioma but not with lung adenocarcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1992;16:259–268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

