The PDE1A-PKCalpha signaling pathway is involved in the upregulation of alpha-smooth muscle actin by TGF-beta1 in adventitial fibroblasts
- PMID: 19672103
- PMCID: PMC2855283
- DOI: 10.1159/000231716
The PDE1A-PKCalpha signaling pathway is involved in the upregulation of alpha-smooth muscle actin by TGF-beta1 in adventitial fibroblasts
Abstract
Background: Increasing evidence has suggested that differentiation of adventitial fibroblasts (AFs) to myofibroblasts plays an important role in arterial remodeling. The molecular mechanisms by which myofibroblast formation is regulated still remain largely unknown. This study aimed to evaluate the role of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 1A (PDE1A) in the formation of adventitial myofibroblasts induced by transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta(1).
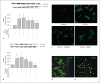
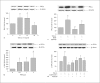
Methods and results: AFs were cultured by the explant method. Western blot and immunocytochemistry were applied for alpha-smooth muscle actin (SMA) or protein kinase C (PKC) alpha protein analysis. Results showed that TGF-beta(1) upregulated PDE1A protein expression in rat aortic AFs and pharmacological inhibition of PDE1A blocked TGF-beta(1)-induced alpha-SMA expression, a marker of myofibroblast formation, suggesting that the upregulation of PDE1A may mediate TGF-beta(1)-induced AF transformation. Moreover, calphostin C (a PKC inhibitor) inhibited TGF-beta(1)-induced alpha-SMA expression, whereas phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (a PKC activator) induced it. Finally, the upregulation of PKCalpha expression by TGF-beta(1) was also inhibited by PDE1A inhibition.
Conclusions: Taken together, our data suggest that TGFbeta(1) induces alpha-SMA expression and myofibroblast formation via a PDE1A-PKCalpha-dependent mechanism. Our study thus unveils a novel signaling mechanism underlying TGF-beta(1)-induced adventitial myofibroblast formation.
Copyright 2009 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differentiation of vascular myofibroblasts induced by transforming growth factor-beta1 requires the involvement of protein kinase Calpha.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2003 Sep;35(9):1105-12. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(03)00207-4. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2003. PMID: 12967633
-
Transforming growth factor-β1 involved in urotensin II-induced phenotypic differentiation of adventitial fibroblasts from rat aorta.Chin Med J (Engl). 2010 Dec;123(24):3634-9. Chin Med J (Engl). 2010. PMID: 22166643
-
Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 1A: a key regulator of cardiac fibroblast activation and extracellular matrix remodeling in the heart.Basic Res Cardiol. 2011 Nov;106(6):1023-39. doi: 10.1007/s00395-011-0228-2. Epub 2011 Oct 20. Basic Res Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 22012077 Free PMC article.
-
Reversal of TGF-β1 stimulation of α-smooth muscle actin and extracellular matrix components by cyclic AMP in Dupuytren's-derived fibroblasts.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011 May 25;12:113. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-12-113. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011. PMID: 21612641 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β1/FGF-2 signaling mediates the 15-HETE-induced differentiation of adventitial fibroblasts into myofibroblasts.Lipids Health Dis. 2016 Jan 5;15:2. doi: 10.1186/s12944-015-0174-3. Lipids Health Dis. 2016. PMID: 26729053 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mining of Potential Biomarkers and Pathway in Valvular Atrial Fibrillation (VAF) via Systematic Screening of Gene Coexpression Network.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Oct 3;2022:3645402. doi: 10.1155/2022/3645402. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Dec 6;2023:9823815. doi: 10.1155/2023/9823815. PMID: 36226239 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Vascular Smooth Muscle Remodeling in Conductive and Resistance Arteries in Hypertension.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Sep;38(9):1969-1985. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311229. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018. PMID: 30354262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic regions associated with muscularity in beef cattle differ in five contrasting cattle breeds.Genet Sel Evol. 2020 Jan 30;52(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12711-020-0523-1. Genet Sel Evol. 2020. PMID: 32000665 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic expression of proteins associated with adventitial remodeling in adventitial fibroblasts from spontaneously hypertensive rats.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010 Oct;31(10):1312-8. doi: 10.1038/aps.2010.88. Epub 2010 Aug 30. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010. PMID: 20802504 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin-3 in Atrial Fibrillation: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Mar 25;19(4):976. doi: 10.3390/ijms19040976. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29587379 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shi Y, Pieniek M, Fard A, O'Brien J, Mannion JD, Zalewski A. Adventitial remodeling after coronary arterial injury. Circulation. 1996;93:340–348. - PubMed
-
- Shen WL, Gao PJ, Che ZQ, Ji KD, Yin M, Yan C, Berk BC, Zhu DL. NAD(P)H oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species regulate angiotensin-II induced adventitial fibroblast phenotypic differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;339:337–343. - PubMed
-
- Sartore S, Chiavegato A, Faggin E, Franch R, Puato M, Ausoni S, Pauletto P. Contribution of adventitial fibroblasts to neointima formation and vascular remodeling: from innocent bystander to active participant. Circ Res. 2001;89:1111–1121. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto S, Gon Y, Takeshita I, Matsumoto K, Maruoka S, Horie T. Transforming growth factor-beta1 induces phenotypic modulation of human lung fibroblasts to myofibroblast through a c-Jun-NH2-terminal kinase-dependent pathway. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163:152–157. - PubMed

