The effects of a secondary task on forward and backward walking in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 19675121
- PMCID: PMC2888719
- DOI: 10.1177/1545968309341061
The effects of a secondary task on forward and backward walking in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
Background: People with Parkinson's disease (PD) often fall while multitasking or walking backward, unavoidable activities in daily living. Dual tasks involving cognitive demand during gait and unfamiliar motor skills, such as backward walking, could identify those with fall risk, but dual tasking while walking backward has not been examined in those with PD, those who experience freezing of gait (FOG), or healthy older controls.
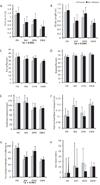
Methods: A total of 78 people with PD (mean age = 65.1 +/-9.5 years; female, 28%) and 74 age-matched and sex-matched controls (mean age = 65.0 +/-10.0 years; female, 23%) participated. A computerized walkway measured gait velocity, stride length, swing percent, stance percent, cadence, heel to heel base of support, functional ambulation profile, and gait asymmetry during forward and backward walking with and without a secondary cognitive task.
Results: Direction and task effects on walking performance were similar between healthy controls and those with PD. However, those with PD were more affected than controls, and freezers were more affected than nonfreezers, by backward walking and dual tasking. Walking backward seemed to affect gait more than dual tasking in those with PD,although the subset of freezers appeared particularly affected by both challenges.
Conclusion: People with PD are impaired while performing complex motor and mental tasks simultaneously,which may put them at risk for falling. Those with FOG are more adversely affected by both motor and mental challenges than those without. Evaluation of backward walking while performing a secondary task might be an effective clinical tool to identify locomotor difficulties.
Figures

References
-
- Melton LJ, III, Leibson CL, Achenbach SJ, et al. Fracture risk after the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease: influence of concomitant dementia. Mov Disord. 2006;21(9):1361–1367. - PubMed
-
- Bacon WE. Secular trends in hip fracture occurrence and survival rate: age and sex differences. J Aging Health. 1996;8:538–553. - PubMed
-
- Bloem BR, Grimbergen YAM, van Dijk JG, Munneke M. The “posture second” strategy: A review of wrong priorities in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sciences. 2006;248:196–204. - PubMed
-
- Horak FB, Dimitrova D, Nutt JG. Direction specific postural instability in subjects with Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol. 2005;198(2):504–521. - PubMed
-
- Bloem BR, Hausdorff JM, Visser JE, Giladi N. Falls and Freezing of Gait in Parkinson’s Disease: A Review of Two Interconnected, Episodic Phenomena. Mov Disord. 2004;19(8):871–884. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

