Quantitative proteomics of seed filling in castor: comparison with soybean and rapeseed reveals differences between photosynthetic and nonphotosynthetic seed metabolism
- PMID: 19675154
- PMCID: PMC2754632
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.109.141622
Quantitative proteomics of seed filling in castor: comparison with soybean and rapeseed reveals differences between photosynthetic and nonphotosynthetic seed metabolism
Abstract
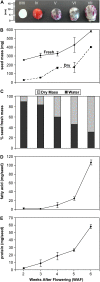
Seed maturation or seed filling is a phase of development that plays a major role in the storage reserve composition of a seed. In many plant seeds photosynthesis plays a major role in this process, although oilseeds, such as castor (Ricinus communis), are capable of accumulating oil without the benefit of photophosphorylation to augment energy demands. To characterize seed filling in castor, a systematic quantitative proteomics study was performed. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis was used to resolve and quantify Cy-dye-labeled proteins expressed at 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 weeks after flowering in biological triplicate. Expression profiles for 660 protein spot groups were established, and of these, 522 proteins were confidently identified by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry by mining against the castor genome. Identified proteins were classified according to function, and the most abundant groups of proteins were involved in protein destination and storage (34%), energy (19%), and metabolism (15%). Carbon assimilatory pathways in castor were compared with previous studies of photosynthetic oilseeds, soybean (Glycine max) and rapeseed (Brassica napus). These comparisons revealed differences in abundance and number of protein isoforms at numerous steps in glycolysis. One such difference was the number of enolase isoforms and their sum abundance; castor had approximately six times as many isoforms as soy and rapeseed. Furthermore, Rubisco was 11-fold less prominent in castor compared to rapeseed. These and other differences suggest some aspects of carbon flow, carbon recapture, as well as ATP and NADPH production in castor differs from photosynthetic oilseeds.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Differential Contribution of Malic Enzymes during Soybean and Castor Seeds Maturation.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 27;11(6):e0158040. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158040. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27347875 Free PMC article.
-
In-depth investigation of the soybean seed-filling proteome and comparison with a parallel study of rapeseed.Plant Physiol. 2008 Sep;148(1):504-18. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.119222. Epub 2008 Jul 3. Plant Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18599654 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of seed filling in Brassica napus. Developmental characterization of metabolic isozymes using high-resolution two-dimensional gel electrophoresis.Plant Physiol. 2006 May;141(1):32-46. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.075390. Epub 2006 Mar 16. Plant Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16543413 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative proteomics of seed maturation in oilseeds reveals differences in intermediary metabolism.Proteomics. 2011 May;11(9):1619-29. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201000644. Epub 2011 Mar 17. Proteomics. 2011. PMID: 21413150 Review.
-
Integration of omics approaches to understand oil/protein content during seed development in oilseed crops.Plant Cell Rep. 2017 May;36(5):637-652. doi: 10.1007/s00299-016-2064-1. Epub 2016 Oct 27. Plant Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 27796489 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic DNA Methylation Analyses Reveal the Distinct Profiles in Castor Bean Seeds with Persistent Endosperms.Plant Physiol. 2016 Jun;171(2):1242-58. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00056. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27208275 Free PMC article.
-
Maize proteomic responses to separate or overlapping soil drought and two-spotted spider mite stresses.Planta. 2016 Oct;244(4):939-60. doi: 10.1007/s00425-016-2559-6. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Planta. 2016. PMID: 27334025 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Contribution of Malic Enzymes during Soybean and Castor Seeds Maturation.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 27;11(6):e0158040. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158040. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27347875 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of oil body membrane proteins accompanying the onset of desiccation phase during sunflower seed development.Plant Signal Behav. 2015;10(12):e1030100. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2015.1030100. Plant Signal Behav. 2015. PMID: 26786011 Free PMC article.
-
Castor Oil: Properties, Uses, and Optimization of Processing Parameters in Commercial Production.Lipid Insights. 2016 Sep 7;9:1-12. doi: 10.4137/LPI.S40233. eCollection 2016. Lipid Insights. 2016. PMID: 27656091 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allen D, Ohlrogge JB, Shachar-Hill Y (2009) The role of light in soybean seed filling metabolism. Plant J 58: 220–234 - PubMed
-
- Alonso AP, Goffman FD, Ohlrogge JB, Shachar-Hill Y (2007) Carbon conversion efficiency and central metabolic fluxes in developing sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) embryos. Plant J 52: 296–308 - PubMed
-
- Baldwin BS, Cossar RD (2008) Castor yield in response to planting date at four locations in the south-central United States. Ind Crops Prod 29: 316–319
-
- Bender-Machado L, Bäuerlein M, Carrari F, Schauer N, Lytovchenko A, Gibon Y, Kelly A, Loureiro M, Müller-Röber B, Willmitzer L, et al (2004) Expression of a yeast acetyl CoA hydrolase in the mitochondrion of tobacco plants inhibits growth and restricts photosynthesis. Plant Mol Biol 55: 645–662 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

