Self-peptides prolong survival in murine autoimmunity via reduced IL-2/IL-7-mediated STAT5 signaling, CD8 coreceptor, and V alpha 2 down-regulation
- PMID: 19675167
- PMCID: PMC2730960
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900793
Self-peptides prolong survival in murine autoimmunity via reduced IL-2/IL-7-mediated STAT5 signaling, CD8 coreceptor, and V alpha 2 down-regulation
Abstract
Although the pathogenic role of B cells and CD4 T cells has been studied extensively, less is known about the role of CD8 T cells in autoimmunity and self-tolerance. To evaluate the role of CD8 T cells in autoimmunity and its modulation using self-peptides, we used mice expressing soluble OVA (sOVA) under control of the keratin-14 promoter. Spontaneous autoimmunity occurred when sOVA mice were crossed with OT-I mice, whose CD8 T cells carry a Valpha2/Vbeta5-transgenic TCR with specificity for the OVA(257-264) peptide. Eighty-three percent of OVA/OT-I mice died during the first 2 wk of life due to multiple organ inflammation. In contrast, preventive or therapeutic OVA(257-264) peptide injections induced a dose-dependent increase in survival. Healthy survivors exhibited reductions in peripheral CD8 T cells, CD8 coreceptor, and Valpha2 expression. Furthermore, CD8 T cells from healthy mice were anergic and could not be activated by exogenous IL-2. A block in IL-2/IL-7 signaling via the STAT5 pathway provided the basis for low surface expression of the CD8 coreceptor and failure of IL-2 to break CD8 T cell anergy. Thus, the soluble TCR ligand triggered multiple tolerance mechanisms in these sOVA/OT-I mice, making this treatment approach a potential paradigm for modulating human autoimmune diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



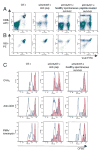
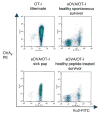
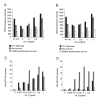
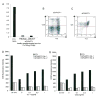
Similar articles
-
Soluble peptide treatment reverses CD8 T-cell-induced disease in a mouse model of spontaneous tissue-selective autoimmunity.J Invest Dermatol. 2012 Mar;132(3 Pt 1):677-86. doi: 10.1038/jid.2011.347. Epub 2011 Nov 17. J Invest Dermatol. 2012. PMID: 22089830 Free PMC article.
-
The use of mouse models to better understand mechanisms of autoimmunity and tolerance.J Autoimmun. 2010 Nov;35(3):192-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2010.06.007. Epub 2010 Jul 23. J Autoimmun. 2010. PMID: 20655706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p59fyn (Fyn) promotes the survival of anergic CD4-CD8- alpha beta TCR+ cells but negatively regulates their proliferative response to antigen stimulation.J Immunol. 2001 Feb 1;166(3):1540-6. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.3.1540. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11160194
-
A model for antigen-specific T-cell anergy: displacement of CD4-p56(lck) signalosome from the lipid rafts by a soluble, dimeric peptide-MHC class II chimera.J Immunol. 2003 Jun 15;170(12):5981-92. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.12.5981. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12794125
-
Interleukin-2, a pro-autoimmune lymphokine that interferes with post-deletional tolerance.Semin Immunol. 1992 Jun;4(3):167-79. Semin Immunol. 1992. PMID: 1627788 Review.
Cited by
-
Soluble peptide treatment reverses CD8 T-cell-induced disease in a mouse model of spontaneous tissue-selective autoimmunity.J Invest Dermatol. 2012 Mar;132(3 Pt 1):677-86. doi: 10.1038/jid.2011.347. Epub 2011 Nov 17. J Invest Dermatol. 2012. PMID: 22089830 Free PMC article.
-
Loureirin B, an essential component of Sanguis Draxonis, inhibits Kv1.3 channel and suppresses cytokine release from Jurkat T cells.Cell Biosci. 2014 Dec 12;4:78. doi: 10.1186/2045-3701-4-78. eCollection 2014. Cell Biosci. 2014. PMID: 25937895 Free PMC article.
-
The use of mouse models to better understand mechanisms of autoimmunity and tolerance.J Autoimmun. 2010 Nov;35(3):192-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2010.06.007. Epub 2010 Jul 23. J Autoimmun. 2010. PMID: 20655706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of CD3+CD4-CD8- T cells as potential regulatory cells in an experimental murine model of graft-versus-host skin disease (GVHD).J Invest Dermatol. 2013 Nov;133(11):2538-2545. doi: 10.1038/jid.2013.212. Epub 2013 May 6. J Invest Dermatol. 2013. PMID: 23648548 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jacobson DL, Gange SJ, Rose NR, Graham NM. Epidemiology and estimated population burden of selected autoimmune diseases in the United States. Clinical immunology and immunopathology. 1997;84:223–243. - PubMed
-
- Annunziato F, Cosmi L, Liotta F, Maggi E, Romagnani S. The phenotype of human T(h)17 cells and their precursors, the cytokines that mediate their differentiation and the role of T(h)17 cells in inflammation. International immunology. 2008;20:1361–1368. - PubMed
-
- Rose NR, Bona C. Defining criteria for autoimmune diseases (Witebsky's postulates revisited) Immunology today. 1993;14:426–430. - PubMed
-
- Yanaba K, Bouaziz JD, Matsushita T, Magro CM, St Clair EW, Tedder TF. B-lymphocyte contributions to human autoimmune disease. Immunological reviews. 2008;223:284–299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

