Corticotropin-releasing factor receptor antagonism within the dorsal raphe nucleus reduces social anxiety-like behavior after early-life social isolation
- PMID: 19675229
- PMCID: PMC2772211
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0854-09.2009
Corticotropin-releasing factor receptor antagonism within the dorsal raphe nucleus reduces social anxiety-like behavior after early-life social isolation
Abstract
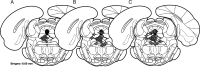
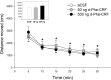
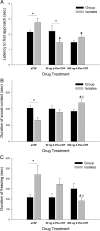
Social isolation of rats during the early part of development increases social anxiety-like behavior in adulthood. Furthermore, early-life social isolation increases the levels of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) receptors in the serotonergic dorsal raphe nucleus (dRN) of adult rats. Interactions between serotonin and CRF systems are thought to mediate anxiety behavior. Therefore, we investigated the effects of CRF receptor antagonism within the dRN on social anxiety-like behavior after early-life social isolation. Male rats were reared in isolation or in groups from weaning until midadolescence, and rehoused in groups and allowed to develop into adulthood. Adult rats underwent surgery to implant a drug cannula into the dRN. After recovery from surgery and acclimation to the testing arena, rats were infused with vehicle or the CRF receptor antagonist d-Phe-CRF((12-41)) (50 or 500 ng) into the dRN before a social interaction test. Isolation-reared rats pretreated with vehicle exhibited increased social anxiety-like behavior compared with rats reared in groups. Pretreatment of the dRN with d-Phe-CRF((12-41)) significantly reduced social anxiety-like behaviors exhibited by isolation-reared rats. Overall, this study shows that early-life social stress results in heightened social anxiety-like behavior, which is reversed by CRF antagonism within the dRN. These data suggest that CRF receptor antagonists could provide a potential treatment of stress-related social anxiety.
Figures
References
-
- Amat J, Tamblyn JP, Paul ED, Bland ST, Amat P, Foster AC, Watkins LR, Maier SF. Microinjection of urocortin 2 into the dorsal raphe nucleus activates serotonergic neurons and increases extracellular serotonin in the basolateral amygdala. Neuroscience. 2004;129:509–519. - PubMed
-
- Andersen SL. Trajectories of brain development: point of vulnerability or window of opportunity? Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2003;27:3–18. - PubMed
-
- Bale TL. Sensitivity to stress: dysregulation of CRF pathways and disease development. Horm Behav. 2005;48:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Clark MS, McDevitt RA, Hoplight BJ, Neumaier JF. Chronic low dose ovine corticotropin releasing factor or urocortin II into the rostral dorsal raphe alters exploratory behavior and serotonergic gene expression in specific subregions of the dorsal raphe. Neuroscience. 2007;146:1888–1905. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
