Attenuation of peripheral salt taste responses and local immune function contralateral to gustatory nerve injury: effects of aldosterone
- PMID: 19675282
- PMCID: PMC2763818
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00219.2009
Attenuation of peripheral salt taste responses and local immune function contralateral to gustatory nerve injury: effects of aldosterone
Abstract
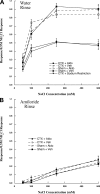
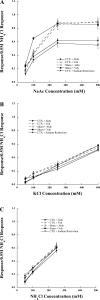
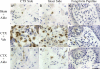
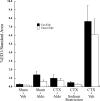
Dietary sodium restriction coupled with axotomy of the rat chorda tympani nerve (CTX) results in selectively attenuated taste responses to sodium salts in the contralateral, intact chorda tympani nerve. Converging evidence indicates that sodium deficiency also diminishes the activated macrophage response to injury on both the sectioned and contralateral, intact sides of the tongue. Because a sodium-restricted diet causes a robust increase in circulating aldosterone, we tested the hypothesis that changes in neurophysiological and immune responses contralateral to the CTX could be mimicked by aldosterone administration instead of the low-sodium diet. Taste responses in rats with CTX and supplemental aldosterone for 4-6 days were similar to rats with CTX and dietary sodium restriction. Responses to sodium salts were as much as 50% lower compared with sham-operated and vehicle-supplemented rats. The group-related functional differences were eliminated with lingual application of amiloride, suggesting that a major transduction pathway affected was through epithelial sodium channels. Consistent with the functional results, few macrophages were observed on either side of the tongue in rats with CTX and aldosterone. In contrast, macrophages were elevated on both sides of the tongue in rats with CTX and the vehicle. These results show that sodium deficiency or administration of aldosterone suppresses the immune response to neural injury, resulting in attenuation of peripheral gustatory function. They also show a potential key link among downstream consequences of sodium imbalance, taste function, and immune activity.
Figures

References
-
- Asher C, Eren R, Kahn L, Yeger O, Garty H. Expression of the amiloride-blockable Na+ channel by RNA from control versus aldosterone-stimulated tissue. J Biol Chem 267: 16061–16065, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Asher C, Wald H, Rossier BC, Garty H. Aldosterone-induced increase in the abundance of Na+ channel subunits. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 271: C605–C611, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Bernstein IL, Taylor EM. Amiloride sensitivity of the chorda tympani response to sodium chloride in sodium-depleted Wistar rats. Behav Neurosci 106: 722–725, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Brown NJ. Aldosterone and vascular inflammation. Hypertension 51: 161–167, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

