Role of mast cells and protease-activated receptor-2 in cyclooxygenase-2 expression in urothelial cells
- PMID: 19675284
- PMCID: PMC2763817
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00310.2009
Role of mast cells and protease-activated receptor-2 in cyclooxygenase-2 expression in urothelial cells
Abstract
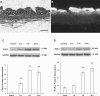
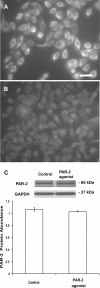
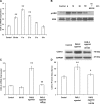
Mast cells have been shown to play a role in development and persistence of various inflammatory bladder disorders. Mast cell-derived tryptase specifically activates protease-activated receptor-2 (PAR-2), and PAR-2 is known to be involved in inflammation. We investigated whether mast cells participate in increase of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) protein abundance in urothelium/suburothelium of bladders of mice subsequent to cyclophosphamide (CYP)-induced bladder inflammation. We also used primary cultures of human urothelial cells to investigate cellular mechanisms underlying activation of PAR-2 resulting in increased COX-2 expression. We found that treatment of mice with CYP (150 mg/kg ip) increased COX-2 protein abundance in bladder urothelium/suburothelium 3, 6, and 24 h after CYP (P < 0.01), and increased COX-2 protein abundance was prevented by treatment of mice with the mast cell stabilizer sodium cromolyn (10 mg/kg ip) for 4 consecutive days before CYP treatment. Incubation of freshly isolated mouse urothelium/suburothelium with a selective PAR-2 agonist, 2-furoyl-LIGRLO-amide (3 microM), also increased COX-2 protein abundance (P < 0.05). We further demonstrated that 2-furoyl-LIGRLO-amide (3 microM) increased COX-2 mRNA expression and protein abundance in primary cultures of human urothelial cells (P < 0.01), and the effects of PAR-2 activation were mediated primarily by the ERK1/2 MAP kinase pathway. These data indicate that there are functional interactions among mast cells, PAR-2 activation, and increased expression of COX-2 in bladder inflammation.
Figures

References
-
- Alagiri M, Chottiner S, Ratner V, Slade D, Hanno PM. Interstitial cystitis: unexplained associations with other chronic disease and pain syndromes. Urology 49, Suppl 5A: 52–57, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Bjorling DE, Jerde TJ, Zine MJ, Busser BW, Saban MR, Saban R. Mast cells mediate the severity of experimental cystitis in mice. J Urol 162: 231–236, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Bon K, Lanteri-Minet M, Michiels JF, Menetrey D. Cyclophosphamide cystitis as a model of visceral pain in rats: a c-fos and Krox-24 study at telencephalic levels, with a note on pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP). Exp Brain Res 122: 165–174, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Boucher W, el-Mansoury M, Pang X, Sant GR, Theoharides TC. Elevated mast cell tryptase in the urine of patients with interstitial cystitis. Br J Urol 76: 94–100, 1995 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

