How thioredoxin dissociates its mixed disulfide
- PMID: 19675666
- PMCID: PMC2714181
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000461
How thioredoxin dissociates its mixed disulfide
Abstract
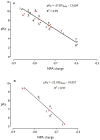
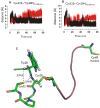
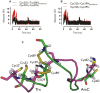
The dissociation mechanism of the thioredoxin (Trx) mixed disulfide complexes is unknown and has been debated for more than twenty years. Specifically, opposing arguments for the activation of the nucleophilic cysteine as a thiolate during the dissociation of the complex have been put forward. As a key model, the complex between Trx and its endogenous substrate, arsenate reductase (ArsC), was used. In this structure, a Cys29(Trx)-Cys89(ArsC) intermediate disulfide is formed by the nucleophilic attack of Cys29(Trx) on the exposed Cys82(ArsC)-Cys89(ArsC) in oxidized ArsC. With theoretical reactivity analysis, molecular dynamics simulations, and biochemical complex formation experiments with Cys-mutants, Trx mixed disulfide dissociation was studied. We observed that the conformational changes around the intermediate disulfide bring Cys32(Trx) in contact with Cys29(Trx). Cys32(Trx) is activated for its nucleophilic attack by hydrogen bonds, and Cys32(Trx) is found to be more reactive than Cys82(ArsC). Additionally, Cys32(Trx) directs its nucleophilic attack on the more susceptible Cys29(Trx) and not on Cys89(ArsC). This multidisciplinary approach provides fresh insights into a universal thiol/disulfide exchange reaction mechanism that results in reduced substrate and oxidized Trx.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- Messens J, Van Molle I, Vanhaesebrouck P, Limbourg M, Van Belle K, et al. How thioredoxin can reduce a buried disulphide bond. J Mol Biol. 2004;339:527–537. - PubMed
-
- Aslund F, Berndt KD, Holmgren A. Redox potentials of glutaredoxins and other thiol-disulfide oxidoreductases of the thioredoxin superfamily determined by direct protein-protein redox equilibria. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:30780–30786. - PubMed
-
- Cheng Z, Arscott LD, Ballou DP, Williams CH., Jr. The relationship of the redox potentials of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase from Drosophila melanogaster to the enzymatic mechanism: reduced thioredoxin is the reductant of glutathione in Drosophila. Biochemistry. 2007;46:7875–7885. - PubMed
-
- Martin JL. Thioredoxin–a fold for all reasons. Structure. 1995;3:245–250. - PubMed
-
- Eklund H, Gleason FK, Holmgren A. Structural and functional relations among thioredoxins of different species. Proteins. 1991;11:13–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

