Comparison of fluid absorption during transurethral resection of prostate and Holmium-Yag laser enucleation of benign adenoma of prostate using breath ethanol concentration
- PMID: 19675787
- PMCID: PMC2721519
- DOI: 10.4103/0970-1591.32061
Comparison of fluid absorption during transurethral resection of prostate and Holmium-Yag laser enucleation of benign adenoma of prostate using breath ethanol concentration
Abstract
Objective: We conducted a study to detect, quantify and compare irrigation fluid absorption in transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) and Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP), using BEC.
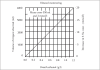
Materials and methods: The study included 50 patients of lower urinary tract symptoms, secondary to benign enlargement of prostate. The patients were nonrandomly allocated to undergo TURP and HoLEP. Twenty-six patients underwent TURP and the remaining 24 underwent HoLEP. Sterile water tagged with 1% ethanol w/v was used for irrigation. Absorption was detected and quantified every 10min by BEC levels. Data was analyzed using standard nomograms.
Results: In HoLEP, 14/24 had no fluid absorption. The remaining 10/24 showed fluid absorption ranging from 95 ml to 300 ml. In TURP, all had fluid absorption ranging from 250-980 ml. Three TURP patients developed overt symptoms, while none did in the HoLEP group.
Conclusions: Fluid absorption observed in our study in the HoLEP group was lower than in the TURP group.
Keywords: Breath ethanol concentration; Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate; fluid absorption; transurethral resection of the prostate.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Mebust WK, Holtgrewe HL, Cockett AT, Peters PC. Transurethral prostatectomy: Immediate and postoperative complications. A cooperative study of 13 participating institutions evaluating, patients 3,885 patients. J Urol. 1989;141:243–7. - PubMed
-
- Weis N, Jorgensen PE, Bruun E. TUR syndrome after Transurethral resection of prostate using suprapubic drainage. Int Urol Nephrol. 1987;19:165–9. - PubMed
-
- Creevy CD. Haemolytic reactions during transurethral prostatic resections. J Urol. 1947;58:125–31. - PubMed
-
- Bazo AE, Greer R, Barnes DG, Kapoor V. Excess fluid absorption with plasmakinetic vaporization of the prostate. BJU Int. 2002;89:971.
-
- Montesinos Baillo A, Banus Gassol JM, Palou Redorta J, Nogueron Castro M, Macias Gimenez N. Pathophysiology and surgical treatment of extravasated peritoneal fluid after Transurethral resection. Eur Urol. 1984;10:183–6. - PubMed