Mathematical modeling and mechanical and histopathological testing of porous prosthetic pylon for direct skeletal attachment
- PMID: 19675985
- PMCID: PMC2905739
- DOI: 10.1682/jrrd.2008.09.0123
Mathematical modeling and mechanical and histopathological testing of porous prosthetic pylon for direct skeletal attachment
Abstract
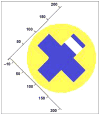
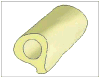
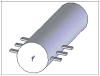
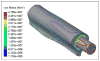
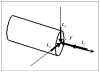
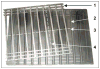
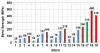
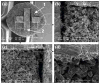
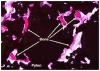
This article presents recent results in the development of the skin and bone integrated pylon (SBIP) intended for direct skeletal attachment of limb prostheses. In our previous studies of the porous SBIP-1 and SBIP-2 prototypes, the bond site between the porous pylons and residuum bone and skin did not show the inflammation characteristically observed when solid pylons are used. At the same time, porosity diminished the strength of the pylon. To find a reasonable balance between the biological conductivity and the strength of the porous pylon, we developed a mathematical model of the composite permeable structure. A novel manufacturing process was implemented, and the new SBIP-3 prototype was tested mechanically. The minimal strength requirements established earlier for the SBIP were exceeded threefold. The first histopathological analysis of skin, bone, and the implanted SBIP-2 pylons was conducted on two rats and one cat. The histopathological analysis provided new evidence of inflammation-free, deep ingrowth of skin and bone cells throughout the SBIP structure.
Figures














References
-
- Brånemark R, Brånemark PI, Rydevik B, Myers RR. Osseo-integration in skeletal reconstruction and rehabilitation: A review. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2001;38(2):175–81. - PubMed
-
- Pitkin M, Blinova MI, Yudintseva NV, Potokin IL, Raykhtsaum G, Pinaev GP. Skin and bone integrated prosthetic technology. I. Characterization and morphology of human cells cultivated on titanium implants of different structures [abstract]. Proceedings of the 9th Russian National Congress, People and Health; 2004 Nov 22–26; St. Petersburg, Russia. St. Petersburg (Russia): Russian National Congress; 2004. p. 217.
-
- Pitkin M, Raykhtsaum G, inventors. Skin integrated device. United States patent US. 20070071788. 2007. Mar 29,
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
