Efflux-mediated drug resistance in bacteria: an update
- PMID: 19678712
- PMCID: PMC2847397
- DOI: 10.2165/11317030-000000000-00000
Efflux-mediated drug resistance in bacteria: an update
Abstract
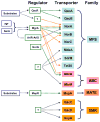
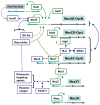
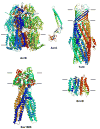
Drug efflux pumps play a key role in drug resistance and also serve other functions in bacteria. There has been a growing list of multidrug and drug-specific efflux pumps characterized from bacteria of human, animal, plant and environmental origins. These pumps are mostly encoded on the chromosome, although they can also be plasmid-encoded. A previous article in this journal provided a comprehensive review regarding efflux-mediated drug resistance in bacteria. In the past 5 years, significant progress has been achieved in further understanding of drug resistance-related efflux transporters and this review focuses on the latest studies in this field since 2003. This has been demonstrated in multiple aspects that include but are not limited to: further molecular and biochemical characterization of the known drug efflux pumps and identification of novel drug efflux pumps; structural elucidation of the transport mechanisms of drug transporters; regulatory mechanisms of drug efflux pumps; determining the role of the drug efflux pumps in other functions such as stress responses, virulence and cell communication; and development of efflux pump inhibitors. Overall, the multifaceted implications of drug efflux transporters warrant novel strategies to combat multidrug resistance in bacteria.
Figures
References
-
- Li X-Z, Nikaido H. Efflux-mediated drug resistance in bacteria. Drugs. 2004;64(2):159–204. - PubMed
-
- Poole K. Efflux-mediated antimicrobial resistance. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005;56(1):20–51. - PubMed
-
- Alekshun MN, Levy SB. Molecular mechanisms of antibacterial multidrug resistance. Cell. 2007;128(6):1037–50. - PubMed
-
- Higgins CF. Multiple molecular mechanisms for multidrug resistance transporters. Nature. 2007;446(7137):749–757. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

