Archaeosomes made of Halorubrum tebenquichense total polar lipids: a new source of adjuvancy
- PMID: 19678953
- PMCID: PMC2739508
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6750-9-71
Archaeosomes made of Halorubrum tebenquichense total polar lipids: a new source of adjuvancy
Abstract
Background: Archaeosomes (ARC), vesicles prepared from total polar lipids (TPL) extracted from selected genera and species from the Archaea domain, elicit both antibody and cell-mediated immunity to the entrapped antigen, as well as efficient cross priming of exogenous antigens, evoking a profound memory response. Screening for unexplored Archaea genus as new sources of adjuvancy, here we report the presence of two new Halorubrum tebenquichense strains isolated from grey crystals (GC) and black mood (BM) strata from a littoral Argentinean Patagonia salt flat. Cytotoxicity, intracellular transit and immune response induced by two subcutaneous (sc) administrations (days 0 and 21) with BSA entrapped in ARC made of TPL either form BM (ARC-BM) and from GC (ARC-GC) at 2% w/w (BSA/lipids), to C3H/HeN mice (25 microg BSA, 1.3 mg of archaeal lipids per mouse) and boosted on day 180 with 25 microg of bare BSA, were determined.
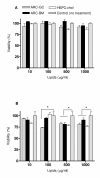
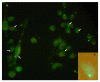
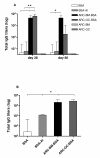
Results: DNA G+C content (59.5 and 61.7% mol BM and GC, respectively), 16S rDNA sequentiation, DNA-DNA hybridization, arbitrarily primed fingerprint assay and biochemical data confirmed that BM and GC isolates were two non-previously described strains of H. tebenquichense. Both multilamellar ARC mean size were 564 +/- 22 nm, with -50 mV zeta-potential, and were not cytotoxic on Vero cells up to 1 mg/ml and up to 0.1 mg/ml of lipids on J-774 macrophages (XTT method). ARC inner aqueous content remained inside the phago-lysosomal system of J-774 cells beyond the first incubation hour at 37 degrees C, as revealed by pyranine loaded in ARC. Upon subcutaneous immunization of C3H/HeN mice, BSA entrapped in ARC-BM or ARC-GC elicited a strong and sustained primary antibody response, as well as improved specific humoral immunity after boosting with the bare antigen. Both IgG1 and IgG2a enhanced antibody titers could be demonstrated in long-term (200 days) recall suggesting induction of a mixed Th1/Th2 response.
Conclusion: We herein report the finding of new H. tebenquichense non alkaliphilic strains in Argentinean Patagonia together with the adjuvant properties of ARC after sc administration in mice. Our results indicate that archaeosomes prepared with TPL from these two strains could be successfully used as vaccine delivery vehicles.
Figures

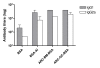
References
-
- Kates M. Archaebacterial lipids: structure, biosynthesis and function. In: Danson MJ, Hough DW, Lunt GG, editor. The Archaebacteria: Biochemistry and Biotechnology. Vol. 58. London: Portland Press and Chapel Hill; 1992. pp. 51–77.
-
- Sprott GD, Tolson DL, Patel GB. Archaeosomes as novel antigen delivery systems. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1997;154:17–22. - PubMed
-
- Sprott GD, CJ D, LP F, GB P. Stability of liposomes prepared from archaeobacterial lipids and phosphatidylcholine mixtures. Cells Mater. 1996;6:143–155.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

