Overexpression of IGF-1 in muscle attenuates disease in a mouse model of spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy
- PMID: 19679072
- PMCID: PMC2735765
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.07.019
Overexpression of IGF-1 in muscle attenuates disease in a mouse model of spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy
Abstract
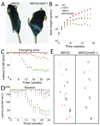
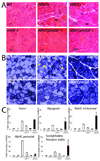
Expansion of a polyglutamine tract in the androgen receptor (AR) causes spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy (SBMA). We previously showed that Akt-mediated phosphorylation of AR reduces ligand binding and attenuates the mutant AR toxicity. Here, we show that in culture insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) reduces AR aggregation and increases AR clearance via the ubiquitin-proteasome system through phosphorylation of AR by Akt. In vivo, SBMA transgenic mice overexpressing a muscle-specific isoform of IGF-1 selectively in skeletal muscle show evidence of increased Akt activation and AR phosphorylation and decreased AR aggregation. Augmentation of IGF-1/Akt signaling rescues behavioral and histopathological abnormalities, extends the life span, and reduces both muscle and spinal cord pathology of SBMA mice. This study establishes IGF-1/Akt-mediated inactivation of mutant AR as a strategy to counteract disease in vivo and demonstrates that skeletal muscle is a viable target tissue for therapeutic intervention in SBMA.
Figures






Comment in
-
IGF-1: elixir for motor neuron diseases.Neuron. 2009 Aug 13;63(3):277-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.07.024. Neuron. 2009. PMID: 19679066
References
-
- Bagriantsev SN, Kushnirov VV, Liebman SW. Analysis of amyloid aggregates using agarose gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 2006;412:33–48. - PubMed
-
- Banno H, Katsuno M, Suzuki K, Takeuchi Y, Kawashima M, Suga N, Takamori M, Ito M, Nakamura T, Matsuo K, et al. Phase 2 trial of leuprorelin in patients with spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Ann Neurol. 2009;65:140–150. - PubMed
-
- Bodine SC, Stitt TN, Gonzalez M, Kline WO, Stover GL, Bauerlein R, Zlotchenko E, Scrimgeour A, Lawrence JC, Glass DJ, Yancopoulos GD. Akt/mTOR pathway is a crucial regulator of skeletal muscle hypertrophy and can prevent muscle atrophy in vivo. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3:1014–1019. - PubMed
-
- Bonuccelli G, Sotgia F, Capozza F, Gazzerro E, Minetti C, Lisanti MP. Localized treatment with a novel FDA-approved proteasome inhibitor blocks the degradation of dystrophin and dystrophin-associated proteins in mdx mice. Cell Cycle. 2007;6:1242–1248. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

