Downregulation of NR3A-containing NMDARs is required for synapse maturation and memory consolidation
- PMID: 19679074
- PMCID: PMC3448958
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.06.016
Downregulation of NR3A-containing NMDARs is required for synapse maturation and memory consolidation
Abstract
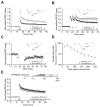
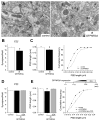
NR3A is the only NMDA receptor (NMDAR) subunit that downregulates sharply prior to the onset of sensitive periods for plasticity, yet the functional importance of this transient expression remains unknown. To investigate whether removal/replacement of juvenile NR3A-containing NMDARs is involved in experience-driven synapse maturation, we used a reversible transgenic system that prolonged NR3A expression in the forebrain. We found that removal of NR3A is required to develop strong NMDAR currents, full expression of long-term synaptic plasticity, a mature synaptic organization characterized by more synapses and larger postsynaptic densities, and the ability to form long-term memories. Deficits associated with prolonged NR3A were reversible, as late-onset suppression of transgene expression rescued both synaptic and memory impairments. Our results suggest that NR3A behaves as a molecular brake to prevent the premature strengthening and stabilization of excitatory synapses and that NR3A removal might thereby initiate critical stages of synapse maturation during early postnatal neural development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures

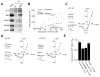



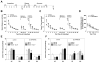

References
-
- Ackermann M, Matus A. Activity-induced targeting of profilin and stabilization of dendritic spine morphology. Nat Neurosci. 2003;6:1194–1200. - PubMed
-
- Al-Hallaq RA, Jarabek BR, Fu Z, Vicini S, Wolfe BB, Yasuda RP. Association of NR3A with the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor NR1 and NR2 subunits. Mol Pharmacol. 2002;62:1119–1127. - PubMed
-
- Bagni C, Greenough WT. From mRNP trafficking to spine dysmorphogenesis: the roots of fragile X syndrome. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6:376–387. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

