Regulation of Fcgamma receptors and immunoglobulin G-mediated phagocytosis in mouse microglia
- PMID: 19679164
- PMCID: PMC2747046
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2009.08.013
Regulation of Fcgamma receptors and immunoglobulin G-mediated phagocytosis in mouse microglia
Abstract
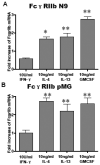
As resident macrophages in the CNS, microglia can transform from a surveillance state to an activated phenotype in response to brain injury. During this transition microglia become highly capable phagocytic cells. Invading pathogens undergo opsonization with immunoglobulins and microglia recognize these opsonized pathogens through interaction with their cognate F(c) receptors. In mice, both FcgammaRI and FcgammaRIIb receptors are involved in IgG-mediated phagocytosis of opsonzied pathogens. At sites of inflammation, microglial activity is regulated by T-cell derived cytokines. Here we first investigated the effects of IFN-gamma, IL-4, IL-13 and GM-CSF on expression of FcgammaRI and FcgammaRIIb mRNA levels in both primary microglia and microglial cell line N9. Using quantitative real-time PCR we show that IFN-gamma induced a 4-fold increase in the mRNA level of FcgammaRI but did not induce changes in FcgammaRIIb expression. IL-4 and IL-13 induced approximately 2-fold increases in expression of FcgammaRIIb mRNA, but had no effect on FcgammaRI expression. GM-CSF increased both FcgammaRI and FcgammaRIIb mRNA expression. We then characterized the ability of these same cytokines to regulate phagocytosis of immune complexes composed of IgG and the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. IFN-gamma and GM-CSF both induced approximately 2-fold increases in IgG-mediated phagocytosis whereas IL-4 and IL-13 both decreased IgG-mediated phagocytosis by about one-third. None of the cytokines influenced basal levels of phagocytosis. These findings demonstrate a highly selective cytokine-induced regulation of both phagocytosis-related Fcgamma receptor subtypes and IgG-mediated phagocytosis itself in microglia. This selective regulation has implications for our understanding of the pathophysiology of CNS infection and autoimmune disease.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of low dose GM-CSF on microglial inflammatory profiles to diverse pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs).J Neuroinflammation. 2007 Mar 20;4:10. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-4-10. J Neuroinflammation. 2007. PMID: 17374157 Free PMC article.
-
GM-CSF, via PU.1, regulates alveolar macrophage Fcgamma R-mediated phagocytosis and the IL-18/IFN-gamma -mediated molecular connection between innate and adaptive immunity in the lung.Blood. 2002 Dec 1;100(12):4193-200. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-04-1102. Epub 2002 Aug 8. Blood. 2002. PMID: 12393686
-
Modulation of Microglial Cell Fcγ Receptor Expression Following Viral Brain Infection.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 6;7:41889. doi: 10.1038/srep41889. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28165503 Free PMC article.
-
Regulated expression and inhibitory function of Fcgamma RIIb in human monocytic cells.J Biol Chem. 2002 Feb 15;277(7):5082-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110277200. Epub 2001 Dec 7. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11741917
-
Microglia in infectious diseases of the central nervous system.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2009 Dec;4(4):448-61. doi: 10.1007/s11481-009-9170-6. Epub 2009 Sep 2. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19728102 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IgM-Dependent Phagocytosis in Microglia Is Mediated by Complement Receptor 3, Not Fcα/μ Receptor.J Immunol. 2015 Dec 1;195(11):5309-17. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401195. Epub 2015 Oct 23. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26500348 Free PMC article.
-
The Functional Roles and Applications of Immunoglobulins in Neurodegenerative Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 26;21(15):5295. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155295. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32722559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-190a potentially ameliorates postoperative cognitive dysfunction by regulating Tiam1.BMC Genomics. 2019 Aug 22;20(1):670. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6035-0. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31438846 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral mechanisms of two broad-spectrum monoclonal antibodies for rabies prophylaxis and therapy.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 10;14:1186063. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1186063. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37638057 Free PMC article.
-
STING inhibition suppresses microglia-mediated synapses engulfment and alleviates motor functional deficits after stroke.J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Apr 8;21(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03086-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 38584255 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bach EA, Aguet M, Schreiber RD. The IFN gamma receptor: a paradigm for cytokine receptor signaling. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997;15:563–591. - PubMed
-
- Bard F, Cannon C, Barbour R, Burke RL, Games D, Grajeda H, Guido T, Hu K, Huang J, Johnson-Wood K, Khan K, Kholodenko D, Lee M, Lieberburg I, Motter R, Nguyen M, Soriano F, Vasquez N, Weiss K, Welch B, Seubert P, Schenk D, Yednock T. Peripherally administered antibodies against amyloid beta-peptide enter the central nervous system and reduce pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. Nat Med. 2000;6:916–919. - PubMed
-
- Barnes N, Gavin AL, Tan PS, Mottram P, Koentgen F, Hogarth PM. FcgammaRI-deficient mice show multiple alterations to inflammatory and immune responses. Immunity. 2002;16:379–389. - PubMed
-
- Cinco M, Domenis R, Perticarari S, Presani G, Marangoni A, Blasi E. Interaction of leptospires with murine microglial cells. New Microbiol. 2006;29:193–199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

