Proton transfer in catalysis and the role of proton shuttles in carbonic anhydrase
- PMID: 19679199
- PMCID: PMC2818086
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2009.08.003
Proton transfer in catalysis and the role of proton shuttles in carbonic anhydrase
Abstract
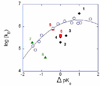
The undisputed role of His64 in proton transfer during catalysis by carbonic anhydrases in the alpha class has raised questions concerning the details of its mechanism. The highly conserved residues Tyr7, Asn62, and Asn67 in the active-site cavity function to fine tune the properties of proton transfer by human carbonic anhydrase II (HCA II). For example, hydrophobic residues at these positions favor an inward orientation of His64 and a low pK(a) for its imidazole side chain. It appears that the predominant manner in which this fine tuning is achieved in rate constants for proton transfer is through the difference in pK(a) between His64 and the zinc-bound solvent molecule. Other properties of the active-site cavity, such as inward and outward conformers of His64, appear associated with the change in DeltapK(a); however, there is no strong evidence to date that the inward and outward orientations of His64 are in themselves requirements for facile proton transfer in carbonic anhydrase.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of hydrophilic residues in proton transfer during catalysis by human carbonic anhydrase II.Biochemistry. 2008 Nov 18;47(46):12028-36. doi: 10.1021/bi801473w. Epub 2008 Oct 23. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18942852 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and kinetic analysis of proton shuttle residues in the active site of human carbonic anhydrase III.Proteins. 2007 Jul 1;68(1):337-43. doi: 10.1002/prot.21403. Proteins. 2007. PMID: 17427958
-
Water networks in fast proton transfer during catalysis by human carbonic anhydrase II.Biochemistry. 2013 Jan 8;52(1):125-31. doi: 10.1021/bi301099k. Epub 2012 Dec 18. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23215152 Free PMC article.
-
Proton transfer function of carbonic anhydrase: Insights from QM/MM simulations.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Feb;1804(2):342-51. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2009.07.026. Epub 2009 Aug 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 19679196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Marcus rate theory applied to enzymatic proton transfer.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 May 12;1458(1):88-103. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(00)00061-x. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. PMID: 10812026 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploration of the residues modulating the catalytic features of human carbonic anhydrase XIII by a site-specific mutagenesis approach.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2019 Dec;34(1):1506-1510. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2019.1653290. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31431090 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Role of Carbonic Anhydrases III and VII in Cellular Defense Mechanisms upon Redox Unbalance.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Aug 5;2018:2018306. doi: 10.1155/2018/2018306. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 30154947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Temperature Effects and Activation Barriers in Aqueous Proton-Uptake Reactions.JACS Au. 2024 Aug 6;4(8):2995-3006. doi: 10.1021/jacsau.4c00326. eCollection 2024 Aug 26. JACS Au. 2024. PMID: 39211613 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of Action of Non-Synonymous Single Nucleotide Variations Associated with α-Carbonic Anhydrase II Deficiency.Molecules. 2019 Nov 4;24(21):3987. doi: 10.3390/molecules24213987. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31690045 Free PMC article.
-
Carbonic anhydrases and their biotechnological applications.Biomolecules. 2013 Aug 19;3(3):553-62. doi: 10.3390/biom3030553. Biomolecules. 2013. PMID: 24970180 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steiner H, Jonsson BH, Lindskog S. Catalytic Mechanism of Carbonic-Anhydrase -Hydrogen-Isotope Effects on Kinetic-Parameters of Human C Isoenzyme. European Journal of Biochemistry. 1975;59:253–259. - PubMed
-
- Tu CK, Silverman DN, Forsman C, Jonsson BH, Lindskog S. Role of histidine 64 in the catalytic mechanism of human carbonic anhydrase II studied with a site-specific mutant. Biochemistry. 1989;28:7913–7918. - PubMed
-
- Silverman DN, Lindskog S. The Catalytic Mechanism of Carbonic-Anhydrase -Implications of a Rate-Limiting Protolysis of Water. Accounts of Chemical Research. 1988;21:30–36.
-
- Chegwidden WR, Carter ND, Edwards YH. The Carbonic Anhydrases New Horizons. Basel: Birkhauser Verlag; 2000.
-
- Supuran CT, Scozzafava A, Conway J. Carbonic Anhydrase - Its Inhibitors and Activators. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2004.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

