Patterns of FGF-23, DMP1, and MEPE expression in patients with chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 19679205
- PMCID: PMC2783834
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bone.2009.08.008
Patterns of FGF-23, DMP1, and MEPE expression in patients with chronic kidney disease
Erratum in
-
Erratum to "Patterns of FGF-23, DMP1, and MEPE expression in patients with chronic kidney disease" [Bone, 45(6) (2009) 1161-1168].Bone. 2018 Mar;108:210-211. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2017.12.019. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Bone. 2018. PMID: 29290423 No abstract available.
Abstract
Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF-23), dentin matrix protein 1 (DMP1), and matrix extracellular phosphoglycoprotein (MEPE) are skeletal proteins involved in the regulation of phosphate homeostasis and bone metabolism. Circulating FGF-23 levels are increased in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD); however, FGF-23 skeletal expression and its regulation by DMP1 and MEPE have yet to be evaluated. Thus, expression of these three proteins was characterized by immunohistochemistry in 32 pediatric and young adult patients with CKD stages 2-5. When compared to normal controls, bone FGF-23 and DMP1 expression were increased in all stages of CKD; significant differences in bone FGF-23 and DMP1 expression were not detected between pre-dialysis CKD and dialysis patients. Bone MEPE expression in CKD did not differ from controls. FGF-23 was expressed in osteocyte cell bodies located at the trabecular periphery. DMP1 was widely expressed in osteocyte cell bodies and dendrites throughout bone. MEPE was also expressed throughout bone, but only in osteocyte cell bodies. Bone FGF-23 expression correlated directly with plasma levels of the protein (r=0.43, p<0.01) and with bone DMP1 expression (r=0.54, p<0.01) and expression of both proteins were inversely related to osteoid accumulation. Bone MEPE expression was inversely related to bone volume. In conclusion, skeletal FGF-23 and DMP1 expression are increased in CKD and are related to skeletal mineralization. The patterns of expression of FGF-23, MEPE, and DMP1 differ markedly in trabecular bone, suggesting that individual osteocytes may have specialized functions. Increases in bone FGF-23 and DMP1 expression suggest that osteocyte function is altered early in the course of CKD.
Figures
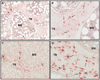
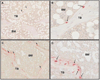
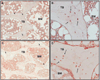
References
-
- Liu S, Rowe PS, Vierthaler L, Zhou J, Quarles LD. Phosphorylated acidic serine-aspartate-rich MEPE-associated motif peptide from matrix extracellular phosphoglycoprotein inhibits phosphate regulating gene with homologies to endopeptidases on the X-chromosome enzyme activity. J Endocrinol. 2007 January;192(1):261–267. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Larsson T, Nisbeth U, Ljunggren O, Jűppner H, Jonsson KB. Circulating concentration of FGF-23 increases as renal function declines in patients with chronic kidney disease, but does not change in response to variation in phosphate intake in healthy volunteers. Kidney Int. 2003 December;64(6):2272–2279. - PubMed
-
- Moe S, Drueke T, Cunningham J, Goodman W, Martin K, Olgaard K, Ott S, Sprague S, Lameire N, Eknoyan G. Definition, evaluation, and classification of renal osteodystrophy: a position statement from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Kidney Int. 2006 June;69(11):1945–1953. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

