Nebulin plays a direct role in promoting strong actin-myosin interactions
- PMID: 19679637
- PMCID: PMC2812046
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.09-137729
Nebulin plays a direct role in promoting strong actin-myosin interactions
Abstract
The role of the actin filament-associated protein nebulin on mechanical and kinetic properties of the actomyosin motor was investigated in skeletal muscle of wild-type (wt) and nebulin-deficient (nebulin(-)(/)(-)) mice that were 1 d old, an age at which sarcomeric structure is still well preserved. In Ca2+-activated skinned fibers from psoas muscle, we determined the Ca2+ dependence of isometric force and stiffness, the rate of force redevelopment after unloaded shortening (k(TR)), the power during isotonic shortening, and the unloaded shortening velocity (V(0)). Our results show a 65% reduction in isometric force in nebulin(-)(/)(-) fibers at saturating [Ca2+], whereas neither thin-filament length nor the Ca2+ sensitivity of the contractile system is affected. Stiffness measurements indicate that the reduction in isometric force is due to a reduction in the number of actin-attached myosin motors, whereas the force of the motor is unchanged. Furthermore, in nebulin(-)(/)(-) fibers, k(TR) is decreased by 57%, V(0) is increased by 63%, and the maximum power is decreased by 80%. These results indicate that, in the absence of nebulin, the attachment probability of the myosin motors to actin is decreased, revealing a direct role for nebulin in promoting strong actomyosin interactions responsible for force and power production.
Figures
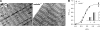

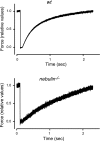


References
-
- Jin J P, Wang K. Nebulin as a giant actin-binding template protein in skeletal muscle sarcomere. Interaction of actin and cloned human nebulin fragments. FEBS Lett. 1991;281:93–96. - PubMed
-
- Wang K, Knipfer M, Huang Q Q, van Heerden A, Hsu L C, Gutierrez G, Quian X L, Stedman H. Human skeletal muscle nebulin sequence encodes a blueprint for thin filament architecture: sequence motifs and affinity profiles of tandem repeats and terminal SH3. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:4304–4314. - PubMed
-
- Littlefield R, Almenar-Queralt A, Fowler V M. Actin dynamics at pointed ends regulates thin filament length in striated muscle. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3:544–551. - PubMed
-
- McElhinny A S, Kolmerer B, Fowler V M, Labeit S, Gregorio C C. The N-terminal end of nebulin interacts with tropomodulin at the pointed ends of the thin filaments. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:583–592. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

